Investigating the impact of analgesic drugs on the risk and treatment of fracture related infection (PanTher)
Background
The management of pain in trauma patients is a necessary and key part of patient care. The medications used in controlling pain may also have an anti-inflammatory effect, which is generally considered beneficial for the patient in the control of pain or post-fracture swelling. Some such medications are considered risk factors for non-union and may also compromise host antibacterial defences.
Goal
Determine if pain management medications have an influence on Fracture related infection (FRI) in rats.
Results
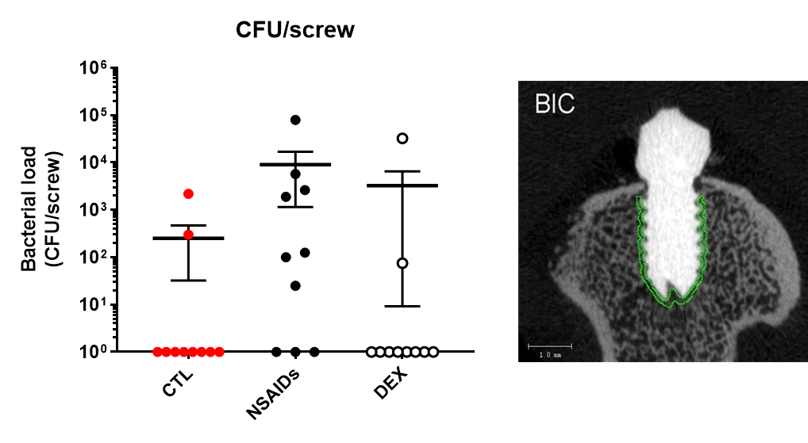
NSAID treatment dramatically affects the efficacy of a combination antibiotic treatment that reliably clears the infection in healthy animals (Figure). Dexamethasone, on the other hand, does not impact upon treatment of FRI. Further investigations are ongoing to evaluate bone related changes by CT between groups, and additional test groups medicated with an opioid.
-
PublicationThompson K, Freitag L, Styger U, Camenisch K, Zeiter S, Arens D, Richards RG, Moriarty TF, Stadelmann VA. Impact of low bone mass and antiresorptive therapy on antibiotic efficacy in a rat model of orthopedic device-related infection. J Orthop Res. 2020;epub Dec 15 https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.24951
Burch MA, Keshishian A, Wittmann C, Nehrbass D, Styger U, Muthukrishnan G, Arens D, Stadelmann VA, Richards RG, Moriarty TF, Thompson K. The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug carprofen negatively impacts new bone formation and antibiotic efficacy in a rat model of orthopaedic-device-related infection. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;41:739-55. https://dx.doi.org/10.22203/eCM.v041a47