Instructing immune system to regenerate musculoskeletal tissues via structurally programmable bio-inks
Background
The musculoskeletal tissue is the framework of our lives. It holds, shapes and supports freedom of movement of our body and protects the crucial internal organs (brain, heart and lungs). It is responsible for our body’s immunity by providing source of stem cells (bone marrow) that readily transform to immune system cells fighting pathogens, so any damage it poses significant threat to the individual’s quality of life. The patient’s immune system does not only play crucial role in fighting various pathogens but is also vital in inducing normal healing of damaged tissues. Patients, especially with prolonged diseases, ranging from diabetes to HIV tend to have decreasing capacity for healing after injuries due to their compromised immune system.
Goal
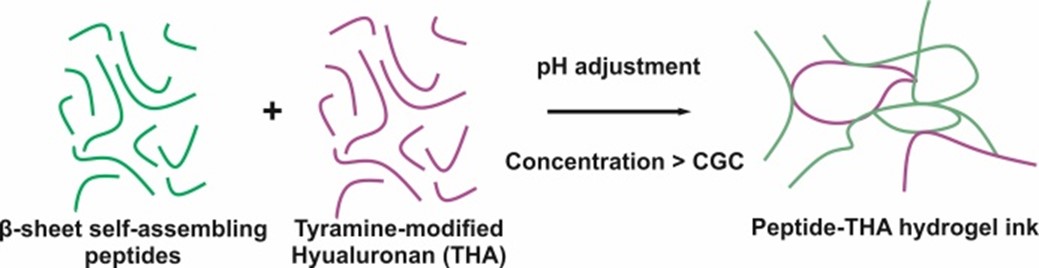
The scope of the EU-funded ImmunoBioInks project is to develop 3D-printed materials to treat musculoskeletal defects in patients with an immune system imbalance. The idea is to combine self-assembling peptides, hyaluronic acid (figure) and nanomaterials into printable scaffolds of defined architecture and with carefully designed mechanical properties that can reprogram the patient’s own immune cells. The interaction of immune cells with this innovative 3D scaffold is expected to trigger the necessary healing response.
Results
A selection of peptide sequences based on the alternation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids: DABACABACD (A: hydrophobic residue: F phenylalanine or Y tyrosine, B/C: hydrophilic residue e.g.: K lysine or E glutamic acid) was designed. A parametric study was then carried out to verify the effect of rational peptide sequence modification on the final physicochemical properties of hydrogels. Tyramine-modified hyaluronan (THA) was also synthesized at two different molecular weights (280 kDa and 1640 kDa) and used to form composite hydrogels with self-assembling peptides. All parental peptides self-assembled into semi-flexible networks and hydrogels above critical gelation concentration in the region of 2.5-5 mM and display characteristic high β-sheet content. Self-assembly, rheological properties and printability of both peptide and peptide-THA hydrogels can be controlled by the choice of primary peptide sequence, fabrication technique and final crosslinking mechanisms including enzymatic (horseradish peroxidase, H2O2) and visible green light crosslinking using Eosin. These hydrogels are characterised by shear-thinning behaviour and rapid recovery allowing extrusion-based fabrication of scaffolds. For the first time we also demonstrate the polarization effects of the supplemented THA on macrophages differentiated from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells over 5 days. M1 and M2 polarization modulated by the supplementation with low and high molecular weight THA were unravelled by the semi-automated image analysis from confocal microscopy, gene expression analysis and ELISA.
In summary here we uncover the link between basic molecular interactions driving self-assembly of functional tyramine modified peptide-based and hyualuronic acid-based biomaterials and demonstrate their capabilities as extrudable platforms for immunomodulatory tissue engineering.
-
PublicationJ. K. Wychowaniec, E.I. Bektas, M. Muerner, J. Sapudom, M. Srejber, M. Airoldi, R. Schmidt, A.J. Vernengo, C.J.C. Edwards-Gayle, P.S. Tipay, M. Otyepka, J. Teo, D. Eglin, M. D'Este. Effect of Tyrosine-Containing Self-Assembling beta-Sheet Peptides on Macrophage Polarization and Inflammatory Response, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 17(19) (2025) 27740-27758.F. Verdugo-Avello, J.K. Wychowaniec, C.A. Villacis-Aguirre, M. D'Este, J.R. Toledo. Bone microphysiological models for biomedical research, Lab Chip 25(5) (2025) 806-836.
J.K. Wychowaniec, E.I. Bektas, A.J. Vernengo, M. Muerner, M. Airoldi, P.S. Tipay, J. Sapudom, J. Teo, D. Eglin, M. D'Este. Effect of molecular weight of tyramine-modified hyaluronan on polarization state of THP-1 and peripheral blood mononuclear cells-derived macrophages, Biomaterials Advances 169 (2025) 214166.
J. Wychowaniec, H. Saini, B. Scheibe, D. Dubal, A Schneemann* and K. Jayaramulu. Hierarchical Porous Metal-organic Gels: From Fundamentals to Potential Applications, Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, Advanced Article.J. Wychowaniec and D. F. Brougham. Emerging magnetic fabrication technologies provide controllable hierarchically-structured biomaterials and stimulus response for biomedical applications, Advanced Science, 2022, 2202278.K. Salma Ancane, A. Sceglovs, E. Tracuma, J. Wychowaniec, Kristine Aunina, A. Ramata-Stunda, V. Nikolajeva, D. Loca, Effect of Crosslinking Strategy on the Biological, Antibacterial and Physicochemical Performance of Hyaluronic Acid and ɛ-Polylysine Based Hydrogels, International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022, 208, 995-1008.C. J. C. Edwards-Gayle and J. Wychowaniec. Characterization of peptide-based nanomaterials, Springer Nature, 2022, accepted, Chapter of book entitled: Peptide Bionanomaterials: From Design to Application.C. Walsh, J. Wychowaniec, D. F. Brougham, D. Dooley, Functional hydrogels as therapeutic tools for spinal cord injury: new perspectives on immunopharmacological interventions, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.108043, Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 2021, 108043.Trivedi Z, Gehweiler D, Wychowaniec JK, Ricken T, Gueorguiev B, Wagner A, Röhrle O. Analysing the bone cement flow in the injection apparatus during vertebroplasty. Proc Appl Math Mech. 2023;23(1): e202200295. https://doi.org/10.1002/pamm.202200295
Trivedi Z, Gehweiler D, Wychowaniec JK, Ricken T, Gueorguiev B, Wagner A, Röhrle O. A continuum mechanical porous media model for vertebroplasty: Numerical simulations and experimental validation. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2023;epub May 12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-023-01715-4
Walsh CM, Wychowaniec JK, Costello L, Brougham DF, Dooley D. An in vitro and ex vivo analysis of the potential of GelMA hydrogels as a therapeutic platform for preclinical spinal cord injury. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;epub Apr 28:e2300951. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202300951Amirian J, Wychowaniec JK, Amel Zendehdel E, Sharma G, Brangule A, Bandere D. Versatile potential of photo-cross-linkable silk fibroin: Roadmap from chemical processing toward regenerative medicine and biofabrication applications. Biomacromolecules. 2023;24(7):2957–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00098
Edwards-Gayle CJC, Wychowaniec JK. Characterization of Peptide-Based Nanomaterials. in: Elsawy MA, editor. Peptide Bionanomaterials. From Design to Application. 2023 Springer, pp. 255-308. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-29360-3_8
Sceglovs A, Wychowaniec JK, Skadins I, Reinis A, Edwards-Gayle CJC, D' Este M, Salma-Ancane K. Effect of steam sterilisation on physico-chemical properties of antibacterial covalently cross-linked ε-polylysine/hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Carbohydrate polymer technologies and applications. 2023;6:100363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2023.100363
Chen B, Benavente LP, Chitto M, Wychowaniec JK, Post V, D'Este M, Constant C, Zeiter S, Feng W, González Moreno M, Trampuz A, Wagemans J, Onsea J, Richards RG, Lavigne R, Moriarty TF, Metsemakers W-J. Alginate microbeads and hydrogels delivering meropenem and bacteriophages to treat Pseudomonas aeruginosa fracture-related infections. Journal of controlled release: official journal of the Controlled Release Society. 2023;364:159-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.10.029
-
Presentation
Design of 3D Printable Supramolecular Self-assembling β-sheet Peptide-hyaluronic acid Hydrogels with Immunomodulatory Properties. TERMIS 2022, Kraków, Poland, 28.06-01.07.2022
Responsive Hydrogels: Towards Spatiotemporally Controllable Biomaterials. RSC Biomaterials Chemistry Group 16th Annual Meeting, London, UK, 10-12.01.2022Rheology – a powerful tool in probing properties of soft biomaterials and Probing nano- and macro-scopic ordering in nanomaterial and biopolymer solutions using small angle X-ray scattering. Baltic Biomaterials Centre of Excellence (BBCE) project, Davos, Switzerland, 23-24.05.2022
From Tuneable Peptide Self-Assembly to Biologically Instructive Materials. MRS 2022 MRS Spring Meeting & Exhibit, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 08-13.06.2022
Probing nano- and macro-scopic ordering in nanomaterial solutions using small angle X-ray scattering. Technical University Dresden, Dresden, Germany (virtual), 30.03.2022
Responsive Hydrogels: Towards Spatiotemporally Controllable Biomaterials. RSC Biomaterials Chemistry Group 16th Annual Meeting, London, UK, 10-12.01.2022
Importance of molecular interactions in controlled molecules delivery. Baltic Biomaterials Centre of Excellence (BBCE) project, Davos, Switzerland, 25.11.2021
3D Printable Supramolecular Self-Assembling β-Sheet Peptide and Tyramine-Modified Hyaluronan Hydrogels with Immunomodulatory Properties. 32nd Annual Meeting of the European Society for Biomaterials, Bordeaux, France, 04-08.09.2022 (poster)
Tyramine-modified supramolecular self-assembling β-sheet peptide and hyaluronan hydrogels. Swiss Society for Biomaterials and Regenerative Medicine (SSBRM) 2022, Zürich, Switzerland, 07.06-09.06.2022 (poster)Mürner M, Bektas EI, Vernengo AJ, Edwards-Gayle CJC, Eglin D, D'Este M, Wychowaniec JK. Effect of tyrosine-including sequence on the physicochemical properties of β-sheet peptide hydrogels. 2023 YSS SSB+RM (poster)
Wychowaniec JK, Bektas EI, Vernengo AJ, Edwards-Gayle CJC, Mürner M, Eglin D, D'Este M. Versatile use of tyramine-modified self-assembling β-sheet peptides and hyaluronic acid hydrogels: from design via 3D printing to immunomodulation. 2023 MRS Spring Meeting (oral)
Wychowaniec JK, Bektas EI, Vernengo AJ, Edwards-Gayle CJC, Mürner M, Teo J, Eglin D, D'Este M. Instructing immune system via structurally programmable tyramine-modified self-assembling β-sheet peptides and hyaluronic acid hydrogels. 2023 ESB (Biomaterials) / (oral)
-
PartnerEglin D (Prof), Mines Saint-Étienne, Univ Lyon, Univ Jean Monnet, INSERM, U1059 Sainbiose, Saint-Étienne, France