Host pathogen interaction in Staphylococcus aureus bone infection
Background
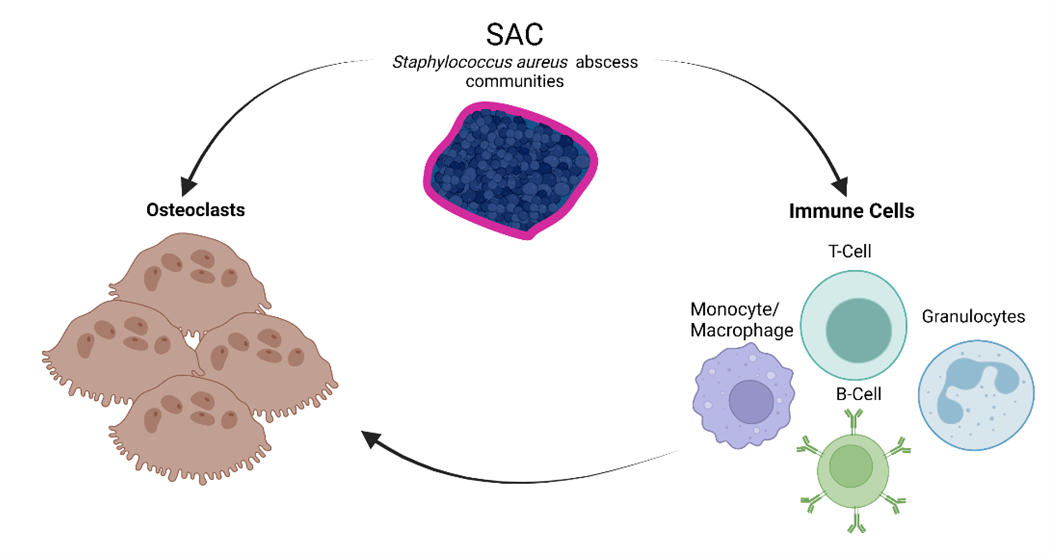
Under normal circumstances, healthy bone has a balanced activity of bone-forming osteoblasts and bone-resorbing osteoclasts. However, during infection, microbial and host factors shift the balance of bone homeostasis in favor of bone destruction. Within bone marrow, Staphylococcus aureus can form so-called staphylococcal abscess communities (SACs) that lie at the center of abscesses and support survival of the bacteria despite local infiltration of immune cells.
Goal
The overarching goal of this project is to understand how the local immune response to SACs leads to bone resorption. Initial experiments will study the effect of SACs on osteoclast formation, function after direct interaction, but also indirectly through co-culture with immune cells.
-
PresentationFehrenbach P, Hofstee MI, Siverino C, Zaat SAJ, de Jong E, Moriarty TF. Staphylococcus aureus abscess community specific host pathogen interaction in bone infection. 2023 YSS SSB+RM (poster)
-
PartnerSebastian A. J. Zaat, Esther C. de Jong; Amsterdam UMC, Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, University of Amsterdam