Biofabrication of cartilage particulate microtissues laden hyaluronan tissue engineered constructs (SSSTC EG 08-122016)
Background
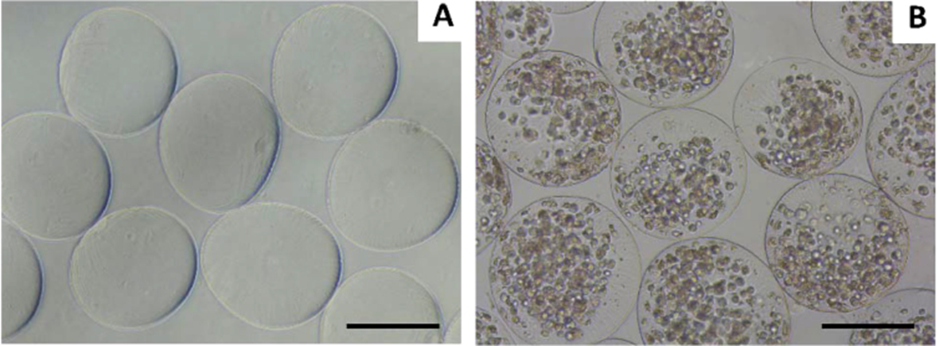
In this project, we optimized the production of electrosprayed human bone marrow stromal cell (hBMSCs)–embedded alginate–gelatin (Alg-Gel,) microspheres for the purpose of their assembly in a 3D-printed poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) scaffold for the fabrication of a mechanically stable and biological supportive tissue engineering cartilage construct. Optimization of hBMSC-embedded Alg-Gel microspheres produced by electrospray has been performed (Figure). The Alg-Gel composition selected allowed the conservation of hBMSC viability and supports proliferation and matrix deposition. The possibility to seed and assemble microspheres in designed 3D-printed PCL scaffolds for the fabrication of a mechanically stable and biological supportive tissue engineering cartilage construct was demonstrated. We optimize and demonstrate that electrospray microsphere fabrication is a cytocompatible and facile process to produce the hBMSC-embedded microsize tissue-like particles that can easily be assembled into a stable construct. This finding could have application in the development of mechanically competent stem cell–based tissue engineering of cartilage regeneration.
Fund:
SSSTC exchange (nr EG 08-122016), Funding: CHF 30'000 Period: 2018-2019.
-
Publication
Xu Y, Peng J, Richards RG, Lu S, Eglin D. (2019). Optimization of electrospray fabrication of stem cell–embedded alginate–gelatin microspheres and their assembly in 3D-printed poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation, 18, 128-141.
-
Partner
Peng J (Prof, MD), the Institute of Orthopedics, Peking Key Lab of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopaedics, Key Lab of Chinese PLA, Chinese PLA General Hospital, People's Republic of China