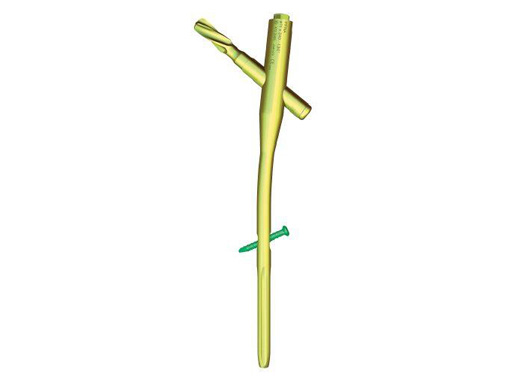
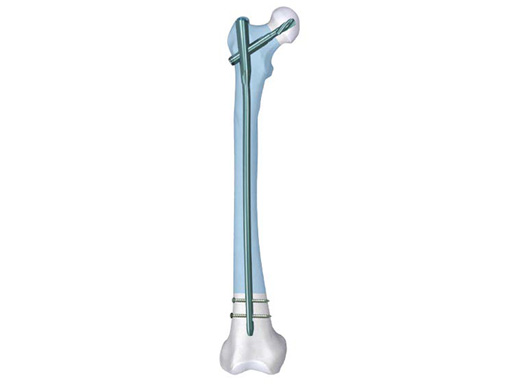
Proximal Femur Nail Antirotation (PFNA)
The PFNA replaces the Proximal Femoral Nail System (PFN) which was developed in 1997 for the treatment of (per)trochanteric fractures. The original PFN allowed fracture stabilization with a load bearing sliding screw and with an additional hip pin for rotational stability of the head-neck fragment. The new PFNA System with the unique spiral blade has a comparable rotational stability as the PFN. This is achieved by compaction of the cancellous bone around the surface of the PFNA blade and results in an excellent fit between the blade and (generally osteoporotic) bone. Current clinical experience proves that the overall complication rate, especially the cut out rate, is low.
The main features of the PFNA system are described as follows:
PFNA (indications)
- Petrochanteric fractures (31-A1 und 31-A2)
- Intertrochanteric fractures (31-A3)
- High subtrochanteric fractures
PFNA long (indications)
- Low and extended subtrochanteric fractures
- Ipsilateral trochanteric and femur shaft fractures
- Pathological fractures
PFNA blade
- Rotational and angular stability achieved with one single element.
- Compaction of cancellous bone for good anchoring of the blade, which is especially important in osteoporotic bone.
- All surgical steps required to insert and lock the blade are done through one lateral incision, which simplifies blade exchance or removal.
PFNA nail
- The PFN design has been proven more than 200,000 times and guarantees an optimal fit of the nail in the femur.
- The medial-lateral angle of 6 allows insertion at the tip of the greater trochanter.
- The PFNA instrumentation offers the possibility of static or dynamic locking for standard and small size nails.
- The flexible nail tip eases insertion and avoids stress concentration distally.
PFNA additional lengths 320–420 mm in SS and TAN
To the existing nails more lengths have been added to 300–420 mm in 20 mm increments for both left and right nails in Ti-6Al-7Nb (TAN) and stainless steel. Those additional lengths have received AO TC approval in 2009. The proximal diameter is 17 mm; the distal diameter varies between 9, 10, 12, and 14 mm. All nails made out of steel come with flutes. The nails out of TAN have flutes for the versions with 12 and 14 mm diameter, the 9 and 10 mm ones are without flutes. All nails are available with two CCD-angles of either 125° or 130° and are cannulated.
PFNA Enhancements
Several components of the PFNA system have been improved to enable intraoperative compression, and facilitate insertion and cleaning. All enhancements have received AO TC approval in December 2010.
Blade
The design has been changed to allow intraoperative compression and to improve the strength of the blade also with respect to implant removal. The current insertion/extraction instrument can be used with the new blade and vice versa because the interface is exactly the same. The new blade can be used with the existing stainless steel insertion handle, or with the existing radiolucent insertion handle. The blade comes in lengths of 75–130 mm in 5 mm increments and is available in titanium and stainless steel. New blade lengths of 75, 125, and 130 mm offer more options to better fit the patients anatomy.
The compression instrument is screwed into the blade through the protection sleeve. Then the buttress nut is turned counterclockwise to move the protection sleeve backwards until it pushes towards the compression instrument. Under image intensifier control, the buttress nut is turned counterclockwise achieving intraoperative compression and closing the fracture gap.
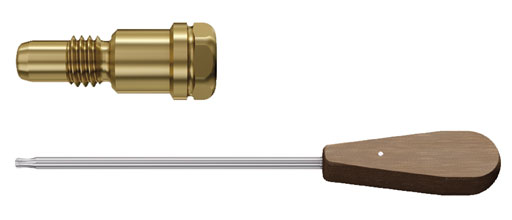
End caps and screwdriver StarDrive
The end caps, available with extensions of 0, 5, 10, or 15 mm in titanium and stainless steel now have a StarDrive T40 recess and are intended for use with a new screwdriver. This new T40 screwdriver has a ball tip which allows angulation of the instrument in relation to the nail/end cap. This facilitates insertion of the end cap over guide wire with hook and is an advantage compared to the current straight T40 screwdriver.
Aiming arm
The new aiming arm is made of PEEK carbon fiber which is easier to clean. It can be used for locking of standard and short nails which reduces the number of instruments needed. The self-holding feature of the protection sleeve makes the handling easier. The new aiming arm is compatible with the existing and new insertion handles.
Insertion handle
Compared to the existing radiolucent handle the new design is slimmer, allowing smaller incisions and therefore reducing potential interference with the pelvis and soft tissues. The handle is radiolucent which provides for good visibility on x-rays. The integrated positioning aids lateral-orientation-facilitated guide-wire positioning and insertion. The new insertion handle is compatible with the existing instruments and implants.
Guide-wire aiming device
This new device facilitates guide-wire positioning and insertion. It is attached to the aiming arm using the connecting screw for PFNA. The C-arm is rotated in AP view until any two orientation lines are symmetrical to the protection sleeve. The midline in between these two orientation lines predicts the location of the guide wire and PFNA blade. The insertion depth of the nail is adapted until the midline is centered in the femoral head. The C-arm may be readjusted to make sure that two lines are symmetrical to the sleeve. The guide-wire aiming device can be attached to the existing aiming arms and also to the new aiming arms.
Locking screw for distal locking
Locking screws for distal locking are now available: either 5.0 mm locking screw, self-tapping in lengths of 28–100 mm, or 5.0 mm locking screw with StarDrive recess in lengths of 26–100 mm.
PFNA/PFNA-II Blade Extraction Set
The PFNA/PFNA-II blade extraction set is a special set containing instruments for the extraction of the PFNA/PFNA-II blade and received its AO TC approval in November 2009. Usually, the blade is removed by the extraction screw for PFNA blade. But in certain cases, especially in younger patients with good bone quality, the PFNA/PFNA-II blade may not be removable with the standard surgical technique and instrumentation. The new extraction set offers special instrumentation for potential issues such as damaged recess of blade, extracted end cap of blade, broken screw, extracted sleeve of blade, and parts of broken instruments in end part of blade.
Proximal Femoral Nail Removal Set
The proximal femoral nail removal set is a comprehensive set containing instruments for the removal of all proximal femoral nails as the trochanteric fixation nail (TFN short, standard, and long), the proximal femoral nail (PFN extra small, small, standard, and long), the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA extra small, small, standard, and long), and PFNA-II (extra small, small, standard, and long). It received AO TC approval in November 2009.
The proximal femoral nail removal set contains general instruments for implant removal as well as all system-specific extraction instruments for the different proximal femoral nails. This prevents abort of surgery due to wrong set order or wrong identification of nailing system and avoids delays caused by missing or incorrect instruments.
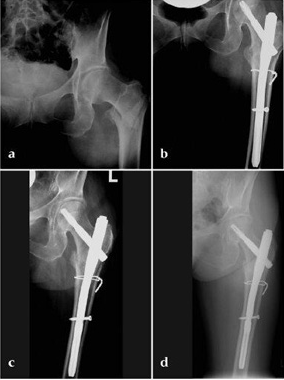
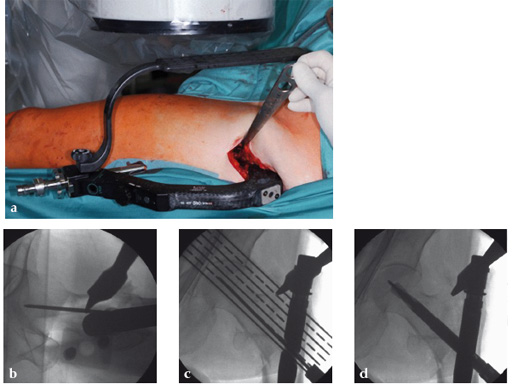
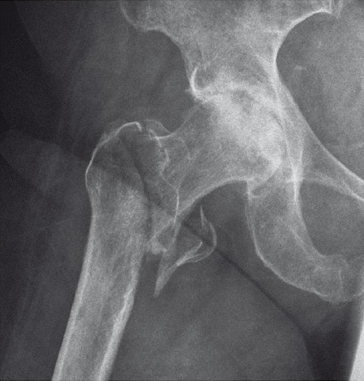
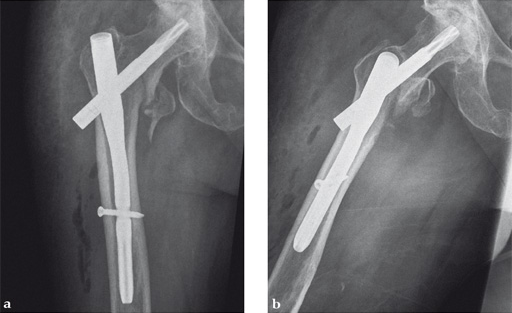
Case 1:
47-year-old female, slipped and fell down the stairs. Traumatic, single 31-A2.1 fracture treated with PFNA.
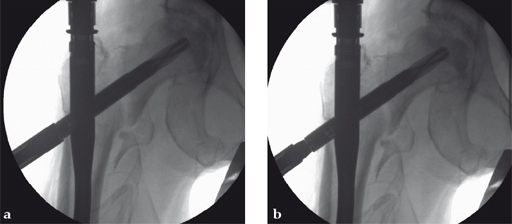
Case 2:
Use of the guide-wire aiming device in an 87-year-old woman.
a Clinical picture of the whole aiming and insertion construct.
b After closed and minimally invasive open reduction with a Hohmann retractor pushing on the anterior aspect of the femoral neck for better axial alignment, the guide-wire aiming device has been mounted to the aiming arm and helps to identify the optimal position of the guide wire in the femoral head.
c The K-wire runs parallel to the chosen line of the aiming device. In AP projection the tip of the blade should be positioned in the center of the femoral head.
d In AP projection the tip of the blade should be positioned in the center of the femoral head, in lateral projection the blade should run parallel to and in middle of the neck and also end dead center of the femoral head. The distance of the tip of the blade to the joint should be approximately 10 mm. No predrilling is recommended in osteoporotic bone.
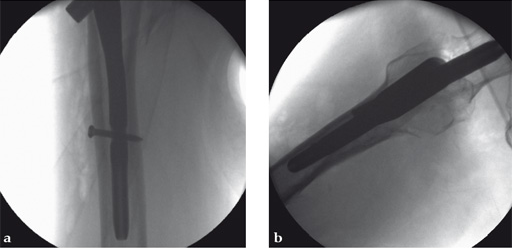
Case 3:
Compression feature used intraoperatively.
Case provided by Michael Blauth, Innsbruck, Austria
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.