Suprapatellar Insertion Instruments
Rami Mosheiff, Matthew Graves
The Suprapatellar Insertion Instruments have been developed in response to the advantages of a suprapatellar nail insertion technique. These instruments allow the insertion of the nail with the leg in extension through the suprapatellar pouch in a simple and intuitive way.
Clinical problem
Extra-articular proximal tibial fractures (AO/type 41A) are fractures involving the proximal tibial segment between the tibial tuberosity and the metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction. These fractures make up 5% to 11% of all tibial fractures. A substantial part of these fractures is caused by high-energy trauma with considerable displacement and comminution.
Three factors have been recognized as causing malalignment in these fractures:
- Muscle pull: Muscle pull on the proximal fragment of the fracture is applied mainly by the patellar tendon. When stressed, as in knee flexion, the anterior part of the proximal fragment is pulled, and thus an anterior angulation is created at the fracture site.
- Nail configuration: The nail, originally designed for midshaft tibial fractures, has a curvature along its proximal third the Herzog bend. This curvature is designed to enable the nail to enter the medullary canal without penetrating the knee joint. Due to this configuration of the tibial nail, both parts of the fracture site are subject to uneven forces. In addition, if the nail impacts the posterior cortex it can create a posterior translational force on the distal fragment. Henley and colleagues termed this phenomenon the wedge effect [1].
- Surgical approach: The medial parapatellar surgical approach of nail insertion can create a slightly medial starting point and lateral entrance angle. As the nail straightens when it meets the lateral cortex, it pushes the proximal fragment into a varus position or the leg into a valgus position. An anterior insertion point causes a similar effect, but in the sagittal plane. The nail is directed down and posteriorly in order to enter the medullary canal. If the entrance angle doesn't match the offset, it creates an apex anterior angulation.
Reference
1) Henley MB, Meier M, Tencer AF (1993) Influences of some design parameters on the biomechanics of the unreamed tibial intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma 7(4): 311-319.
Suprapatellar nail insertion technique
In the last couple of years, significant efforts have been made to change the configuration of the nail to allow accurate reduction and fixation of proximal tibia fractures. These efforts successfully resulted in the Expert Tibial Nail, which is ideal for fractures of this sort. On the other hand, experience shows that the nail itself cannot solve the entire problem without dealing with the other malalignment factors. The suprapatellar insertion technique is a new, innovative technique whose purpose is to neutralize these other factors.
A suprapatellar nail insertion technique will help to reduce the secondary deformities associated with the forces of the tendon pulling on the proximal segment of tibia fractures. The forces are decreased due to the leg being in extension when applying a suprapatellar nail insertion technique. In addition, the new technique, which allows for a high entry point, reduces the medial or lateral deviation of the nail. This new entry point minimizes the risk for angulation in the proximal fracture site during nail insertion.
Suprapatellar Insertion Instruments
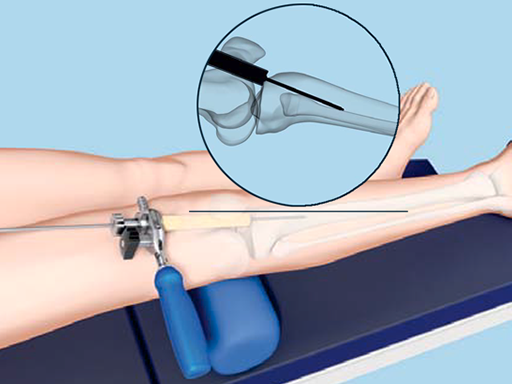
In response to the advantages of a suprapatellar insertion technique, and the increasing clinical demand to perform such a procedure, the Suprapatellar Insertion Instruments have been developed. These instruments allow the insertion of the nail with the leg in extension through the suprapatellar pouch in a simple and intuitive way. The instruments comprise a soft and flexible outer protection sleeve made of santoprene (single-use) to protect the cartilage and soft tissues during the procedure, as well as a metal inner protection sleeve to encompass the cutting and reaming tools and protect the outer protection sleeve. Fig 1 illustrates the insertion of the guide wire after placement of the protection sleeve during the surgical procedure. Adjustments to the guide wire location can be dialed-in by rotating the multi-hole centering sleeve to place a second guide wire while the first guide wire remains in place.
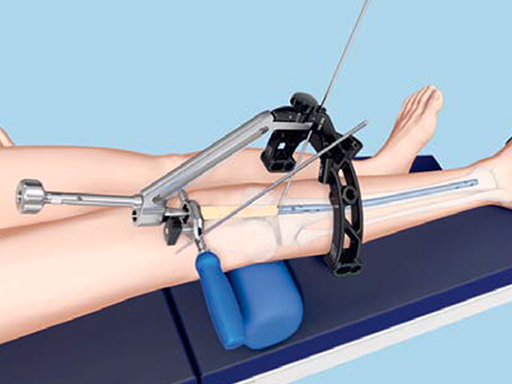
In addition to the Suprapatellar Insertion Instruments, a new carbon fiber aiming arm has been developed and introduced into the tibial nailing systems (Fig 2).
Based on clinical experiences collected over a number of years, the semi-extended position provides multiple advantages for intramedullary rodding, including:
- Elimination of sagittal plane deforming forces in proximal tibial fractures
- Providing a more stable platform for reduction of tibia fractures
- Eliminating the need to change the position of the leg for radiographs, thus decreasing radiation exposure and easing the work of the c-arm technician.
The Suprapatellar Insertion Instruments were designed to take advantage of this experience, while still providing in-line access to the coronal plane anatomic axis.
Latest advances in IM nailing techniques
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.