VOLT™ Mini Fragment and VOLT Small Fragment Plating Systems
Christoph Sommer, Karl Stoffel, Andrew Sands, Cong Feng Luo, Ulrich Stöckle, Michael Swords, Takeshi Sawaguchi, Mark Lee, Mauricio Kfuri,
Harry Hoyen, Jonathan Dwyer, Thomas Fischer, Brian Saunders
Developed by the Next Generation Plating Task Force of the AO Technical Commission in collaboration with Johnson & Johnson MedTech, the Variable Angle Optimized Locking Technology (VOLT™) Mini and Small Fragment Plating Systems are instrument and implant sets intended for the internal fixation of bones and bone fragments of the appendicular skeleton appropriate for the implant size. The main objective of the Task Force was to create a robust system with exceptional locking performance and stability for a wide range of implant shapes and sizes in both stainless steel and titanium.
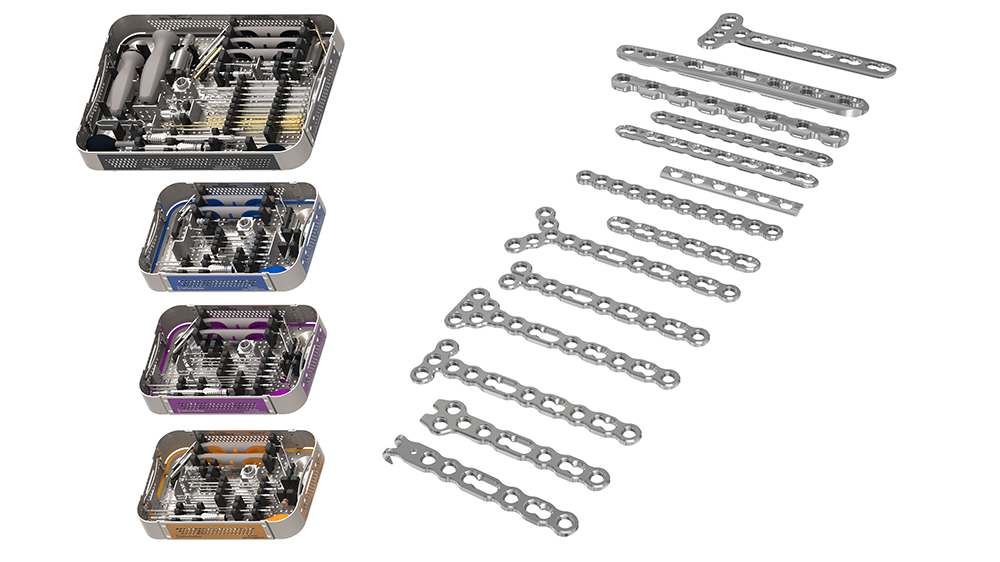
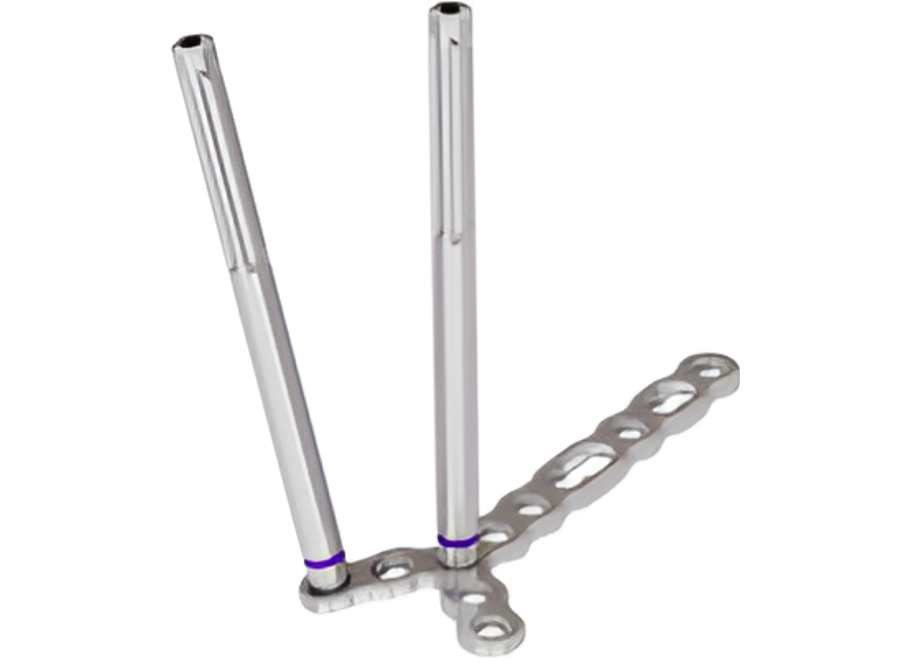
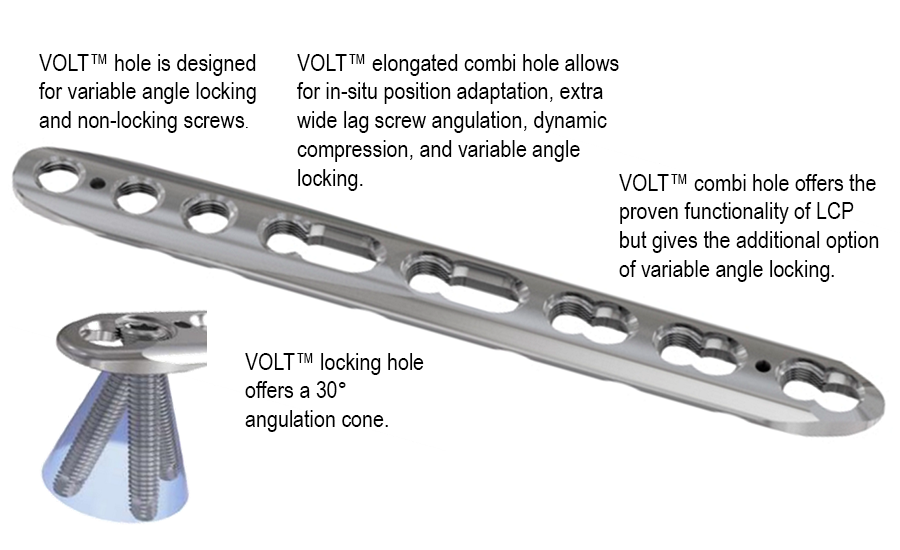
The VOLT™ system features new variable angle locking technology while maintaining the proven Dynamic Compression Unit (DCU). It delivers the stability of the Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system and the flexibility of the Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA-LCP) system. The VOLT™ System includes mini (2.0 mm, 2.4 mm, and 2.7 mm) and small (3.5 mm, and 4.0 mm) fragment generic plates and VA locking, cortex, and cancellous screws (Figs 1–5) as well as instruments for open reduction and internal fixation of bone fragments.
VOLT™ implants are available in stainless steel and titanium in all sizes.
System description
Both the Mini Fragment and Small Fragment Plating Systems are intended for adults, children (2–12 years), and adolescents (12–21 years) in which growth plates (physes) have fused, or in which unfused growth plates will not be compromised by fixation.
The indication is such that the plating systems support auxiliary plating techniques and education. Instructions for use and surgical technique are available from Johnson & Johnson MedTech with details of indications, contraindications, side effects, warnings, and precautions.
The new plates are designed to offer various options regarding plate shape and profile as well as hole density appropriate to different fracture patterns. The instrument functionality has been improved and a consistent look and feel has been implemented to ensure ease of use.
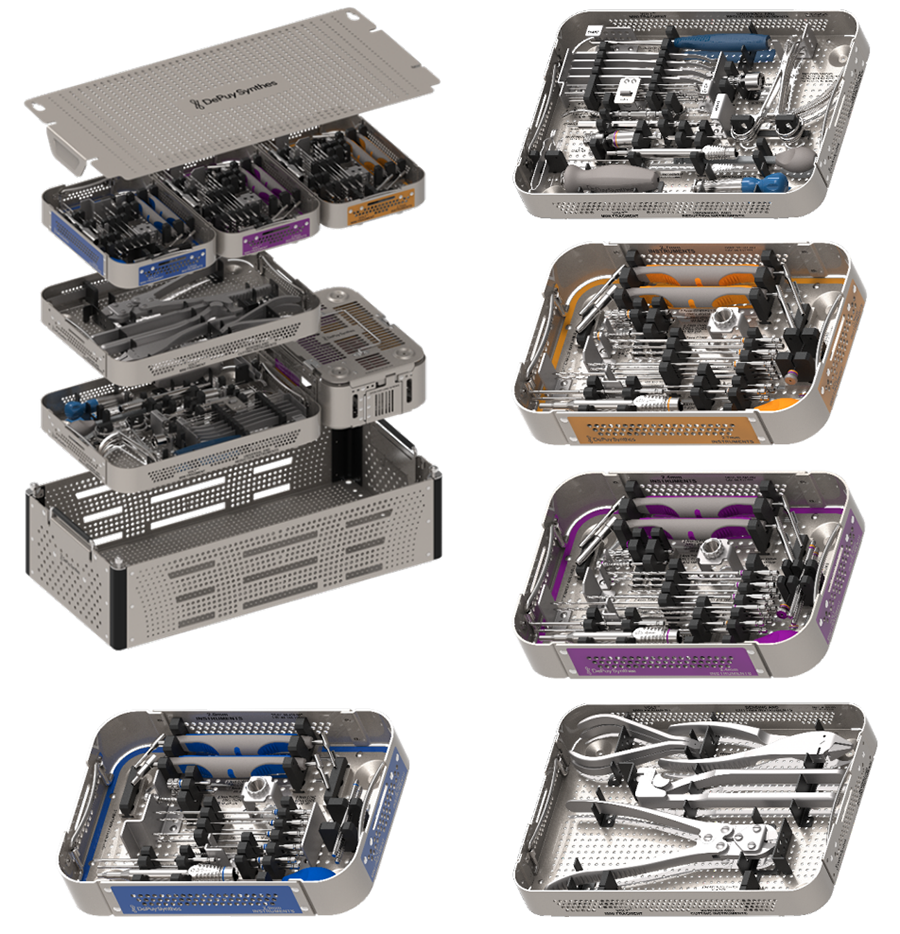
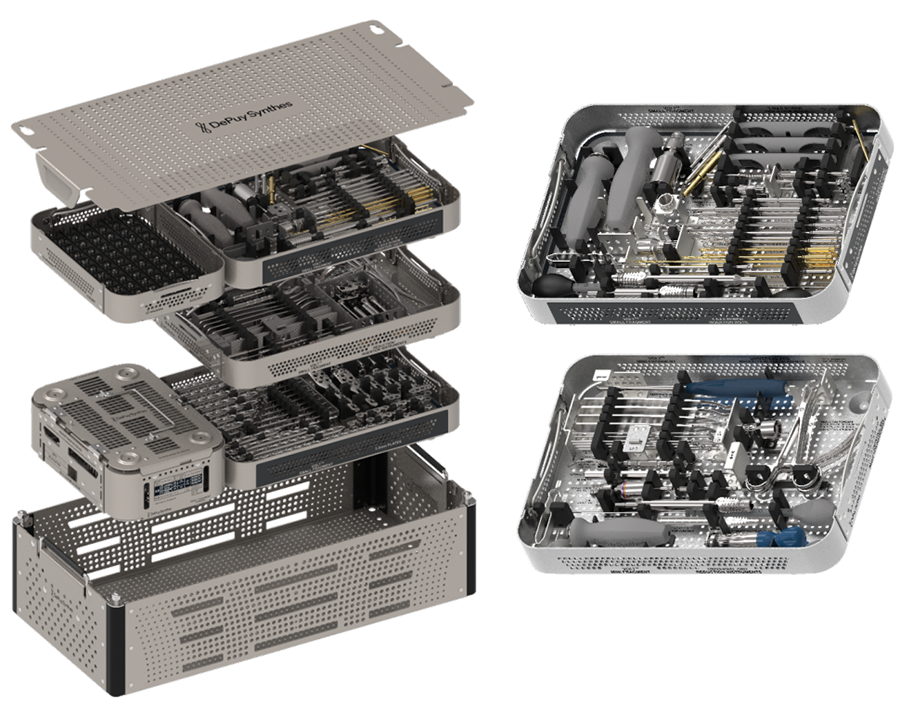
The Mini Fragment and Small Fragment Plating Systems are designed in a modular way, to be assembled according to customers’ preferences. Color-coded universal and size-specific instrument and implant trays support the surgeon and the tech staff in choosing the right instruments for the selected plates.
VOLT locking technology
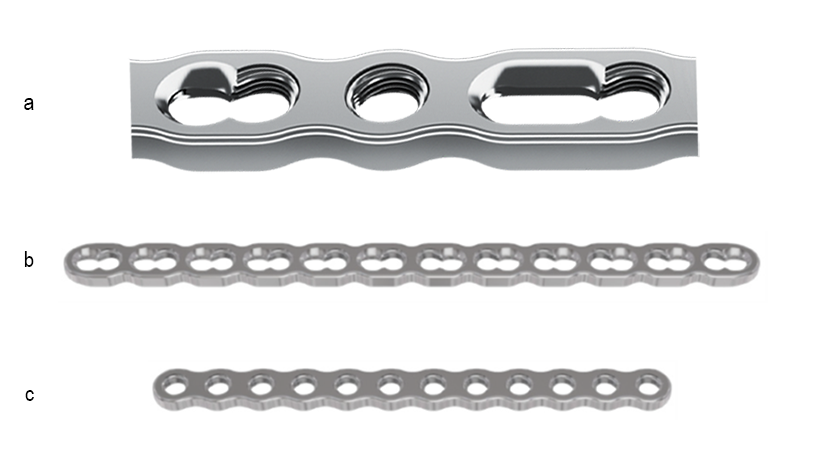
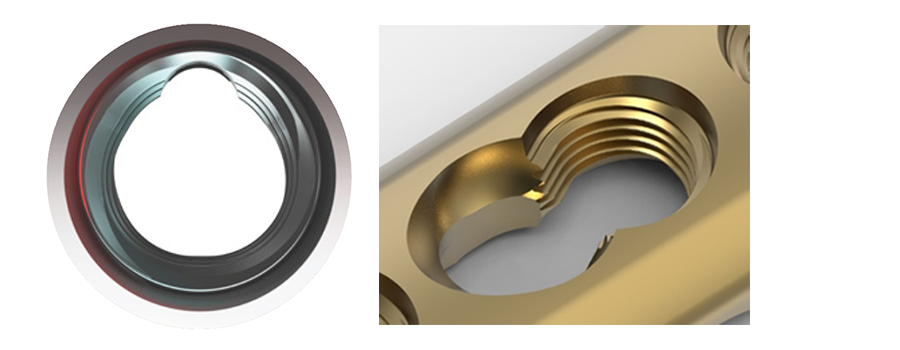
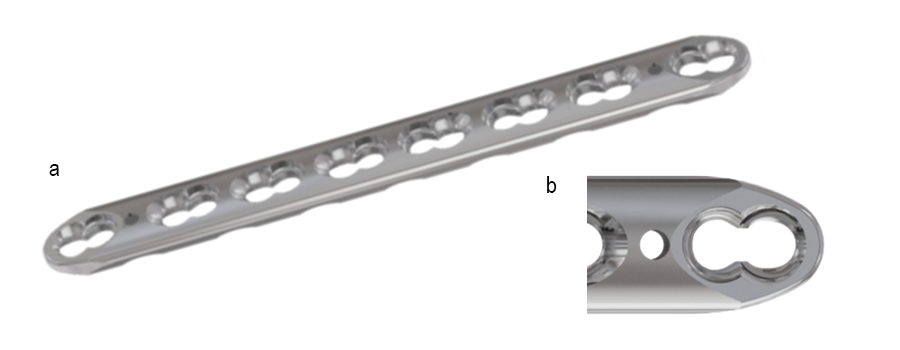
A key innovation of the VOLT platform is the novel variable angle locking technology (Figs 6-7). The VOLT holes appear round but actually have a subtle triangular shape with threads that are precisely engineered with tight manufacturing tolerances. The unique shape of the VOLT holes enables the plate threads to adapt to the screw threads as the screw is inserted. The result is excellent plate to screw engagement and robust cantilever strength. The technology allows for a screw angulation of up to 15°, hence a locking cone of 30°.
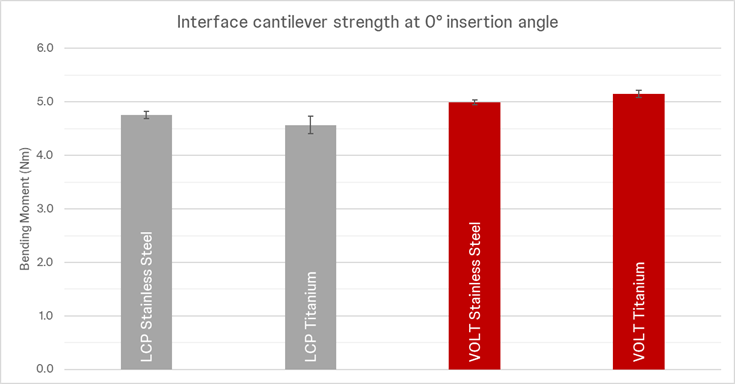
The cantilever strength of a VOLT plate/screw (2.4 mm, 2.7 mm, 3.5 mm) interface at nominal (0°) is equivalent to the LCP plate/screw interface at nominal (0°), yet VOLT delivers variable angle capability (Static Cantilever Strength; Fig 8). Thus, the VOLT technology combines the advantages of an LCP with the option of variable angle locking technology. Also, the new combi holes benefit from the VOLT locking technology in the locking part of the combi hole.
All VOLT hole types accept the use of either locking or cortex and cancellous screws. Accordingly, the same fixation principles apply as with previous LCP and VA-LCP systems, facilitating education and transition to VOLT.
Screws
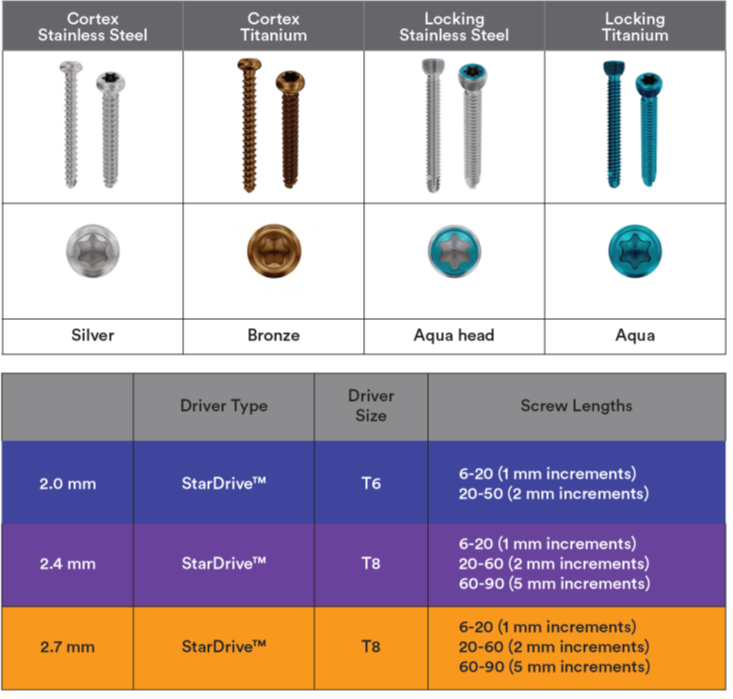
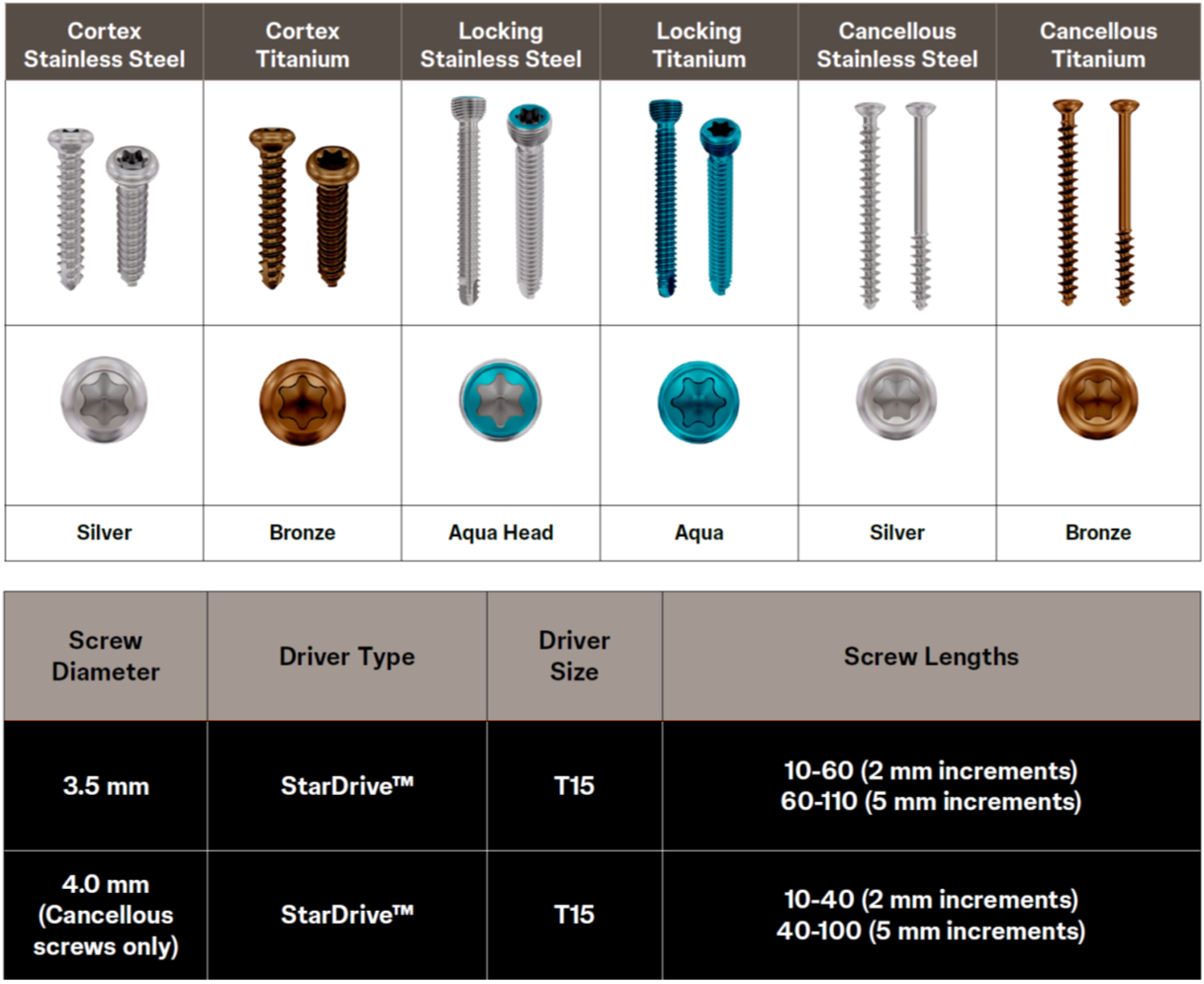
A combination of locking, cortex, and cancellous screws offers versatile options tailored to the VOLT plates. To streamline the surgical steps, instruments are color-coded according to screw diameter. Additionally, a single- or double-band etching assists in identifying complementary parts.
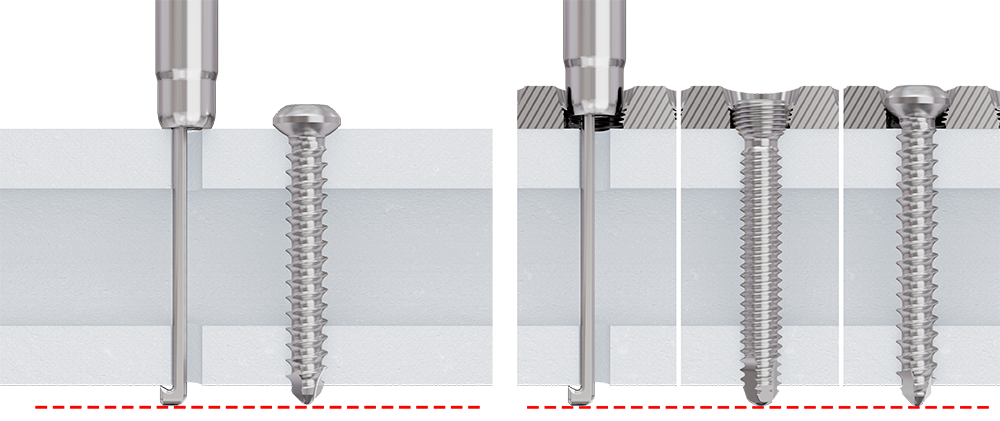
Screws, equipped with an optimized Stardrive recess design (Fig 9), along with new screwdrivers, are intended to enhance the user experience. In addition to the optimized recess design, cortical and cancellous screws have lower profile heads compared to previous designs due to soft-tissue considerations.
The locking screws are designed for locking performance, while offering cutting flutes for ease of insertion and a rounded screw tip (Fig 9), both designed to reduce the risk of soft-tissue irritation.
In the VOLT Small Fragment system, the 4.0 mm cancellous screw offers better hold in the bone compared to the 3.5 mm cortical screw and remains an important fixation option in epi-metaphyseal zones. To support removal, the cancellous shaft screw features back-cutting flutes.
The system offers longer screws compared to its predecessor, providing greater versatility (2.0 mm: up to 50 mm; 2.4 mm and 2.7 mm: up to 90 mm; 3.5 mm: up to 110 mm).
Plates
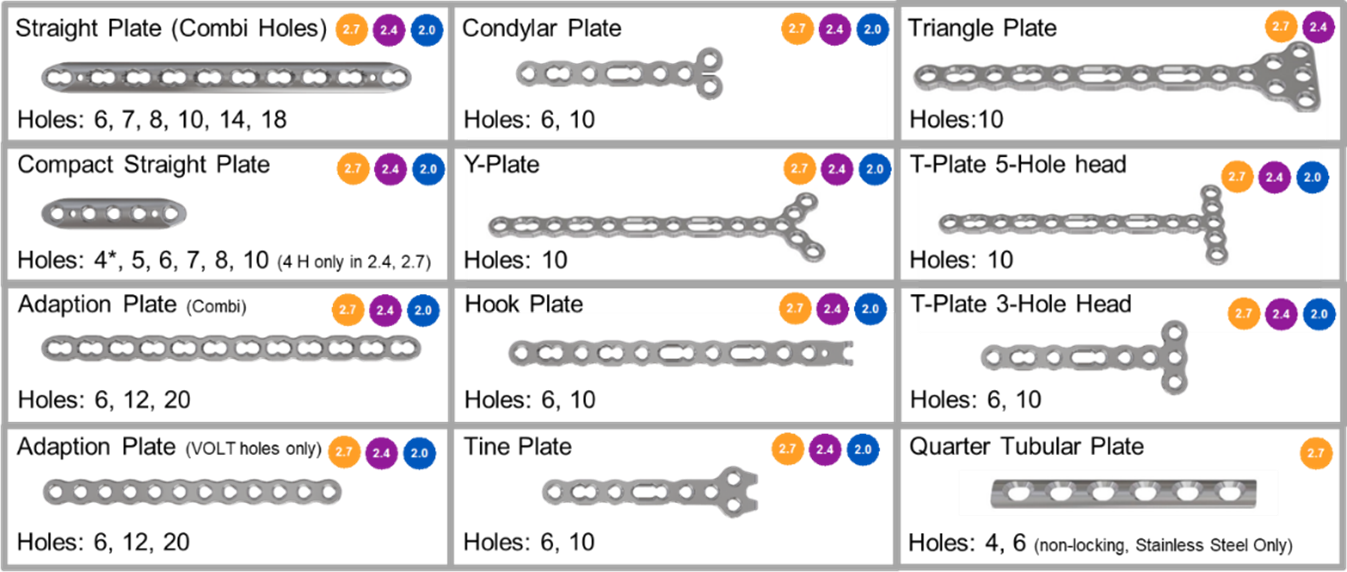
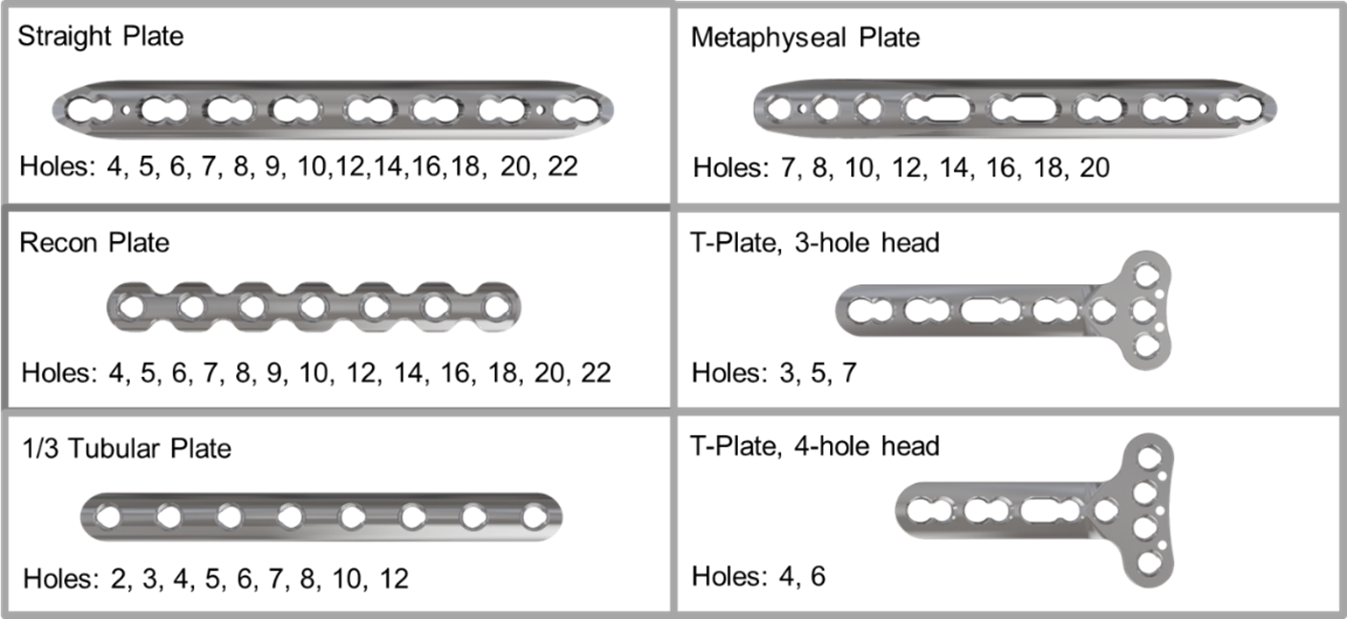
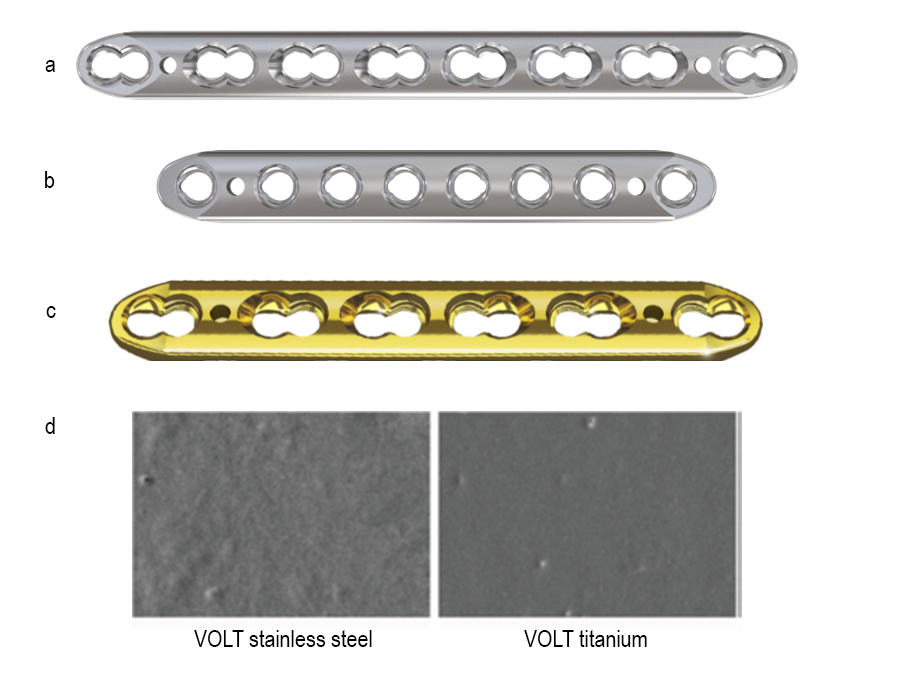
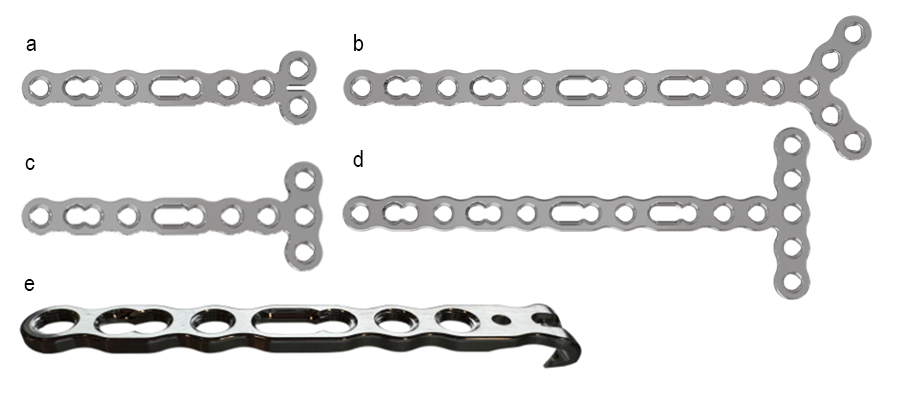
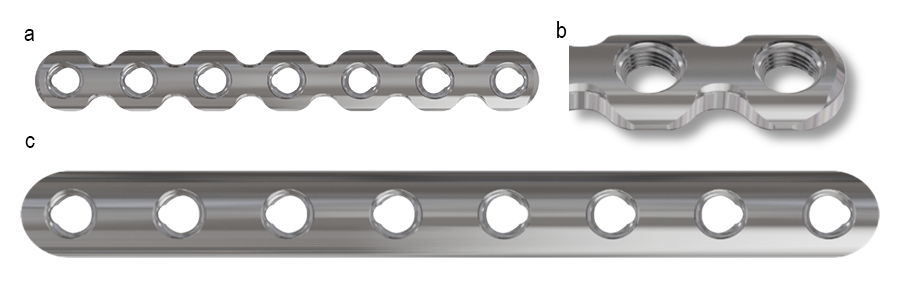
The VOLT Mini and Small Fragment Plating Systems feature a wide range of generic plates (Figs 1-2) . Generic plates, also called non-anatomic or utility plates, are a key pillar in trauma surgery due to their adaptability and versatile application as primary fixation or as an auxiliary fixation device to other implants. All new generic plates feature VOLT technology (Fig 10a-c).
Several new plate shapes and lengths have been introduced. Design features on the plates such as rounded profiles and tapered tips are beneficial as they respect soft tissue and can be used in less invasive surgical techniques. VOLT plate shapes and screw hole patterns are intended to optimize plate function, whether for locking, compression, or buttressing, ensuring efficacy and stability in various orthopedic applications. Furthermore, plate options with increased screw hole density are available, offering more fixation options and thereby providing surgeons with greater flexibility and precision to meet daily fracture fixation challenges.
VOLT titanium plates and screws are anodized and then treated with an electropolish finish. Electropolishing the titanium plates and screws produces a surface texture (Fig 10d) similar to stainless steel. This smooth surface finish reduces bony ongrowth and soft-tissue adhesion, which has been shown to ease implant removal.
Plate types and features
Straight plates
Straight plates (Fig 11) are available for all sizes and are optimized for strength. The proven plate undercuts from LC-DCP and LCP are maintained to give the plate a widely uniform stiffness, supporting continuous bending while limiting contact with the bone when applied with non-locking screws (Fig 11a). While keeping the rounded, smooth tip to support less invasive insertion, holes are also placed close to the ends of the plate, offering a wide fixation range (Fig 11b). Two K-wire holes give an additional option for temporary fixation. The 2.0 mm, 2.4 mm, and 2.7 mm plates are also available in a compact version.
Mini Fragment generic plates
Adaption plates
Adaption plates (Fig 12a) offer the surgeon greater freedom to adapt the plate to specific anatomical situations. Accordingly, they are optimized to allow in-plane, out-of-plane, and torsional bending and cutting to trim the plate to the length needed. Additional focus was given to producing a low and smooth plate profile as these plates are often used in soft-tissue critical zones. Depending on the adaption plate type, the plates offer the VOLT hole, combi hole, elongated combi hole. or a combination thereof. Adaption plates were developed for sizes 2.0 mm, 2.4 mm, and 2.7 mm.
Straight adaption plates
These plates are available with a combi hole and in a compact version (Fig 12b-c). The plates are offered in a length of up to 20 holes.
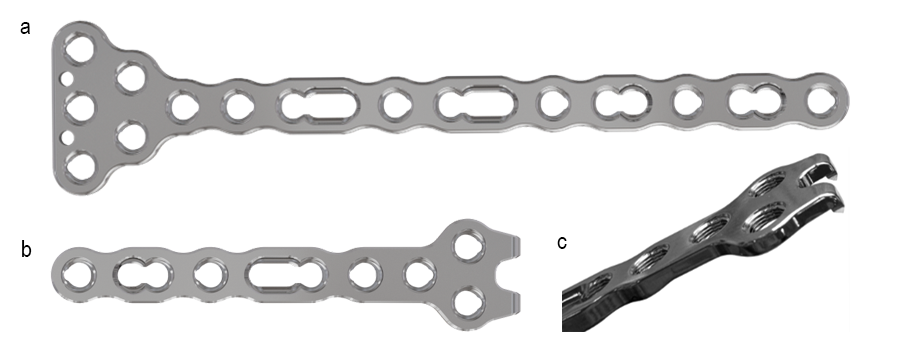
Condylar, Y, and T plates
These plates feature a head element (Fig 13a-d) and are suited for fracture situations where additional fixation options are required.
Hook plates
The hook plate’s adaptability and sharp hooks (Fig 13e) allow the plate to grab and hold small fracture fragments close to a joint and compress them to the shaft. A recess between the hooks supports the secure placement of a cortical screw if needed.
Triangle plates
The triangle plate (Fig 14a) is designed to offer a broader buttressing surface with multiple fixation options. Therefore, the plate has a triangular head shape.
Tine plates
The tine plate (Fig 14b) was developed to give a broader buttress surface and to offer additional support to hold small fragments. Therefore, the plate features a two-hole wide head and two tines that grab the bone (Fig 14c).
Small Fragment generic plates
Metaphyseal plate 3.5 mm
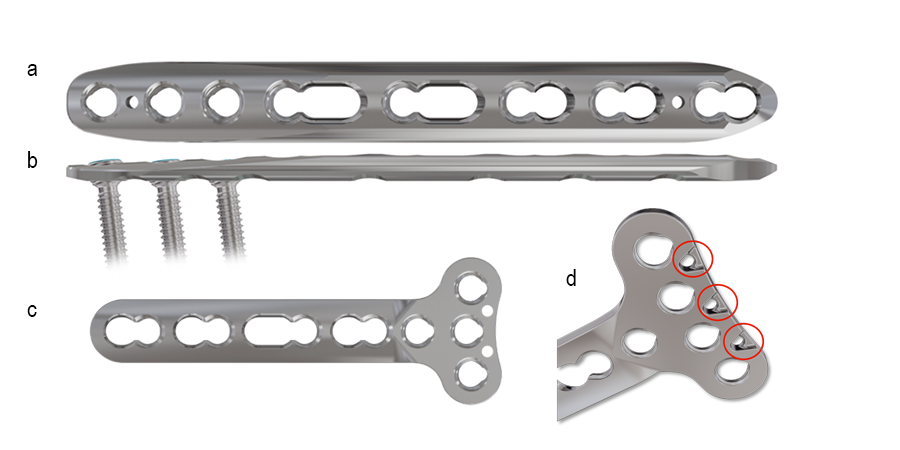
The long taper at the tip of the metaphyseal plate 3.5 mm (Fig 15a) supports buttressing techniques and plate adaption to different anatomies as well as having a low prominence (Fig 15b) considering the often delicate soft-tissue situation. There are three VOLT holes that have an initial screw trajectory of 7° that accommodate plate bending to avoid the joint surface. The longer plates also contain two elongated holes in case of fractures extending into the shaft. The shaft of the plate otherwise offers the same characteristics as the straight small fragment plate.
T plate 3.5 mm
The VOLT T-Plate (Fig 15c) is a thin flat plate, intended mainly for buttressing applications in multiple different indications. The plate is offered with a 4- and 3-hole T section. Frequently used close to joints, the plate is designed with K-wire holes with undercuts to facilitate suturing (Fig 15d).
Reconstruction plate
The versatile reconstruction plate (Fig 16a-b) is designed for situations where bending in different planes is required. It is therefore optimized for in- and out-of-plane bending and for torsional bending, while broadly keeping hole functionality.
1/3 Tubular plate
The 1/3 tubular plate (Fig 16c) maintains its position as a key implant in today’s surgery. Of critical importance was the integration of VOLT technology to incorporate the advantages of VA locking fixation into the plate, while maintaining the elastic properties and thinness of current plates.
Instruments
Instrument handling is critical for successful surgical outcomes and must be intuitive and simple. Therefore, great efforts were made to improve instrument handling during the development of the VOLT Mini and Small Fragment Plating Systems. Key points are highlighted here.
Provisional fixation options
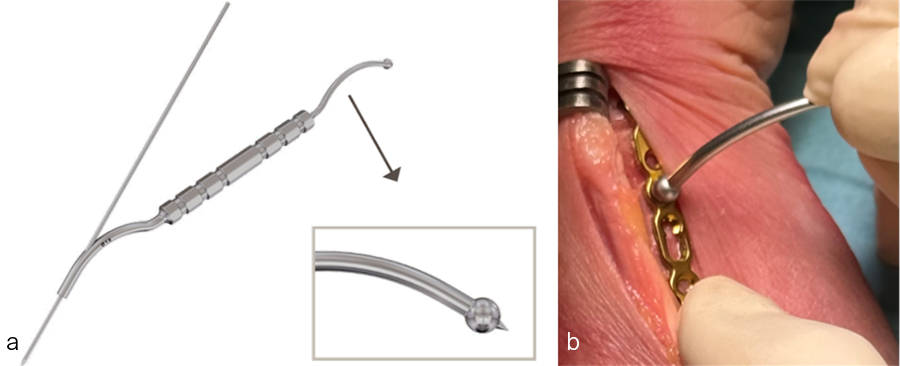
Forceps, K-wires, plate reduction wires, or compression wires can be used to provisionally position and fix the plate to the bone prior to screw insertion (Fig 17a–c).
Fracture reduction can be performed using visualization, if necessary, with or without fluoroscopy. After reduction, fragments are stabilized as needed with implants, K-wire(s), the innovative cannulated fragment reduction tool (Fig 18a–b), or reduction forceps. Alternatively, the fracture can be reduced using the plate by means of non-locking screws in the combi or elongated combi holes. In addition to forceps with a standard rachet (Fig 19a), VOLT offers three new forceps with long rachets, that can provide a wider span (Fig 19b–c).
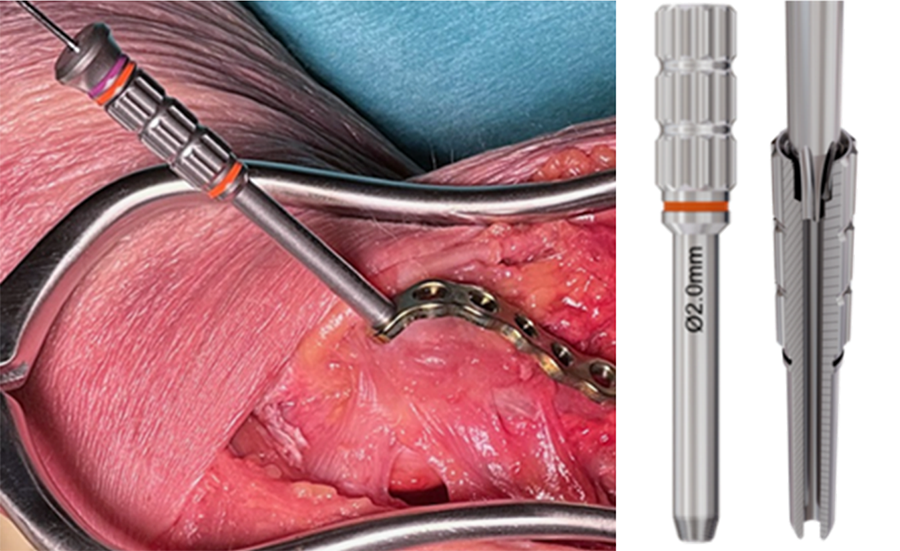
Depth gauge and measurement
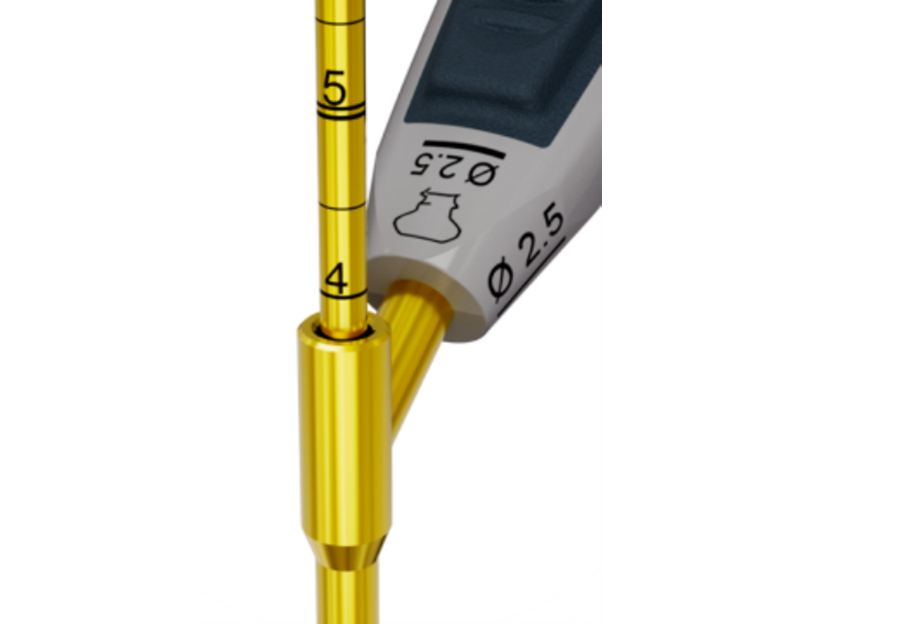
The VOLT depth gauges are color-coded according to screw diameter and are available in different lengths. The depth gauges feature a new tip shape designed to improve hook engagement on the far cortex for accurate and reliable measurements. Independent of the measuring situation, screw size, and screw type, the depth gauge reliably measures the length of the screw needed without additional calculations (Fig 20).
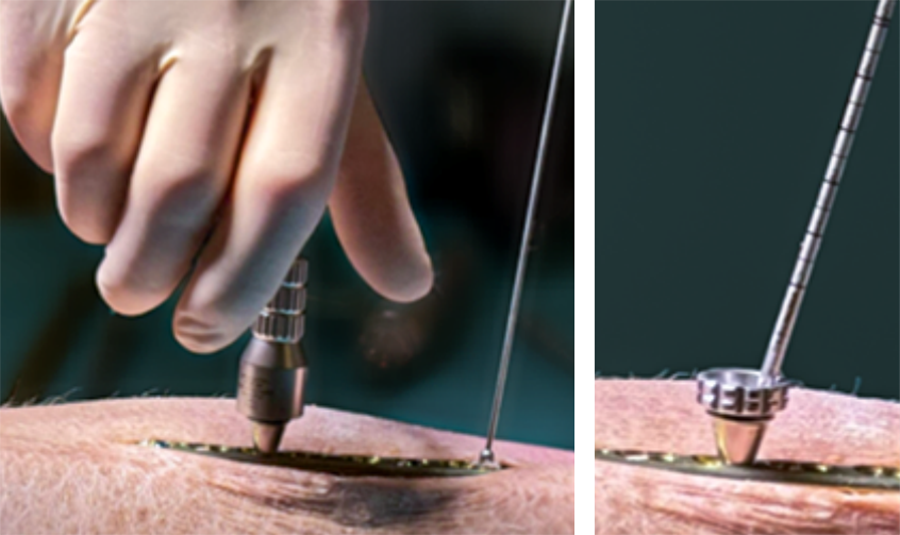
Additionally, the depth gauge is designed to support different handling preferences (Fig 21a–b).
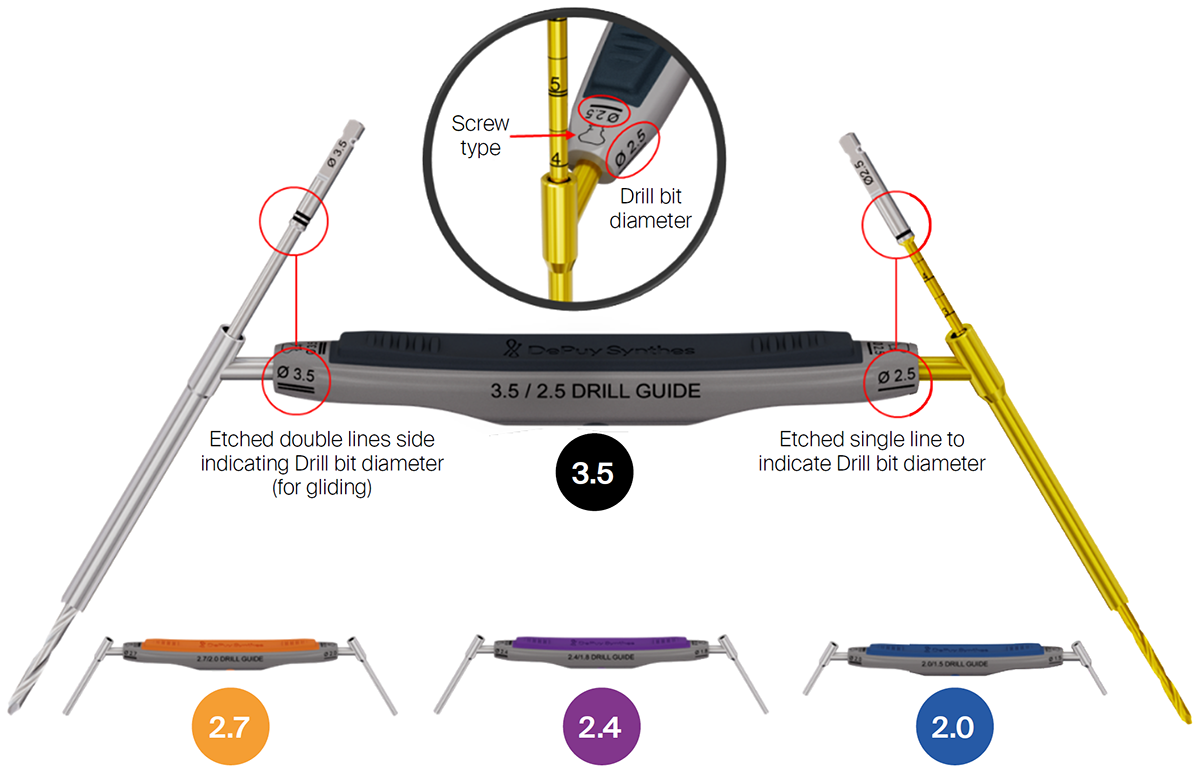
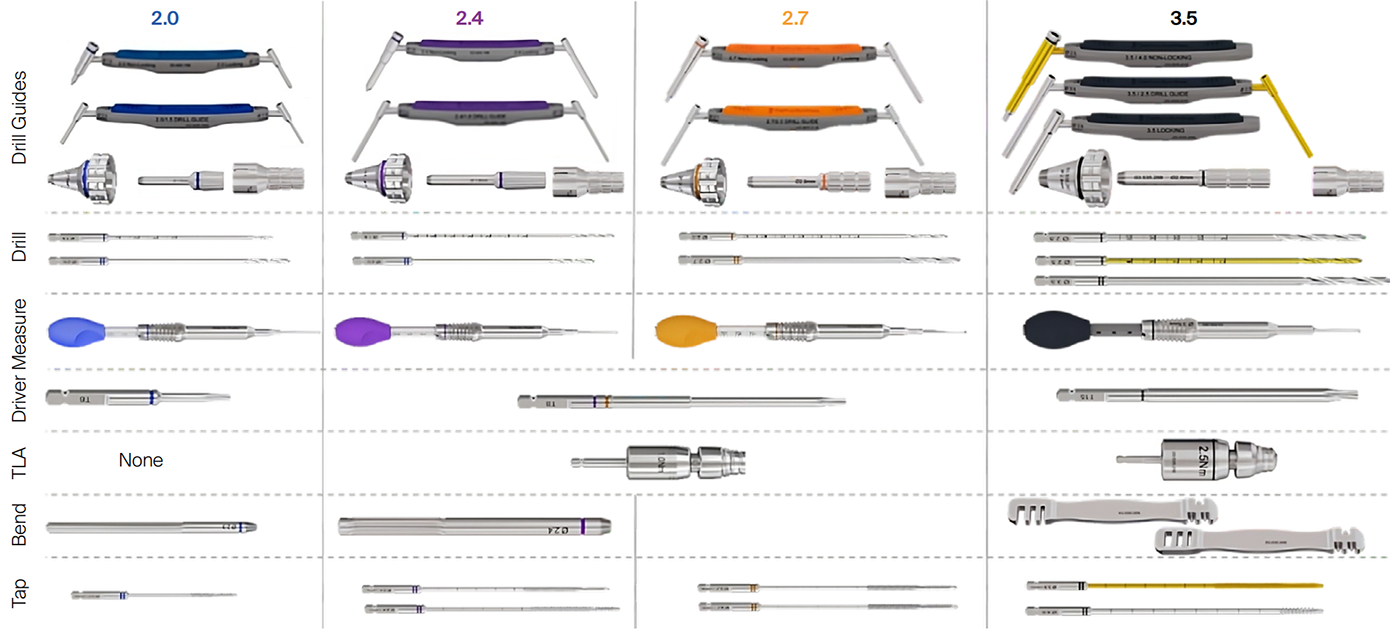
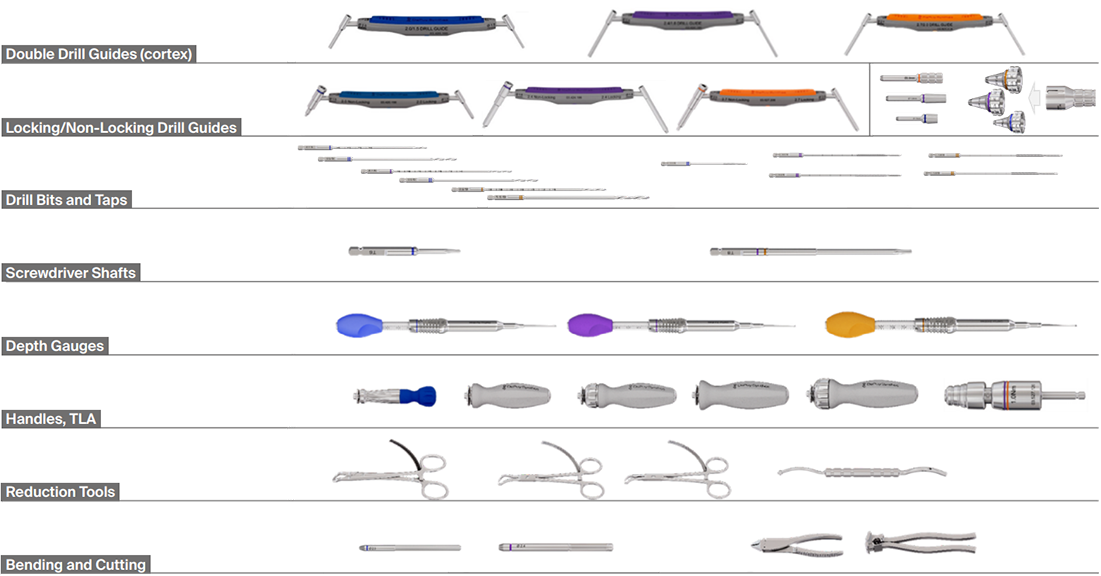
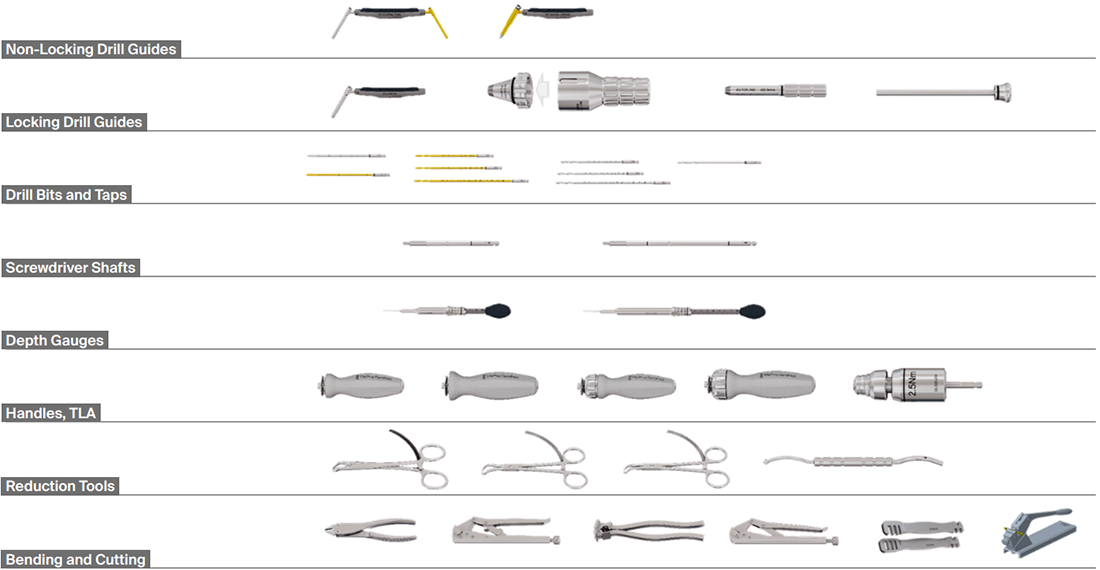
Drill bits and drill guides
A key focus is the handling of the drill and mating drill guides. Both the screw type and the drill bit diameters are displayed. The marking features are standardized across the VOLT system.
The VOLT drill bits are available in short and long lengths. Calibration numbers are clearly etched on them. To simplify reading, each number is etched twice onto the drill bit to make it visible regardless of the position of the drill.
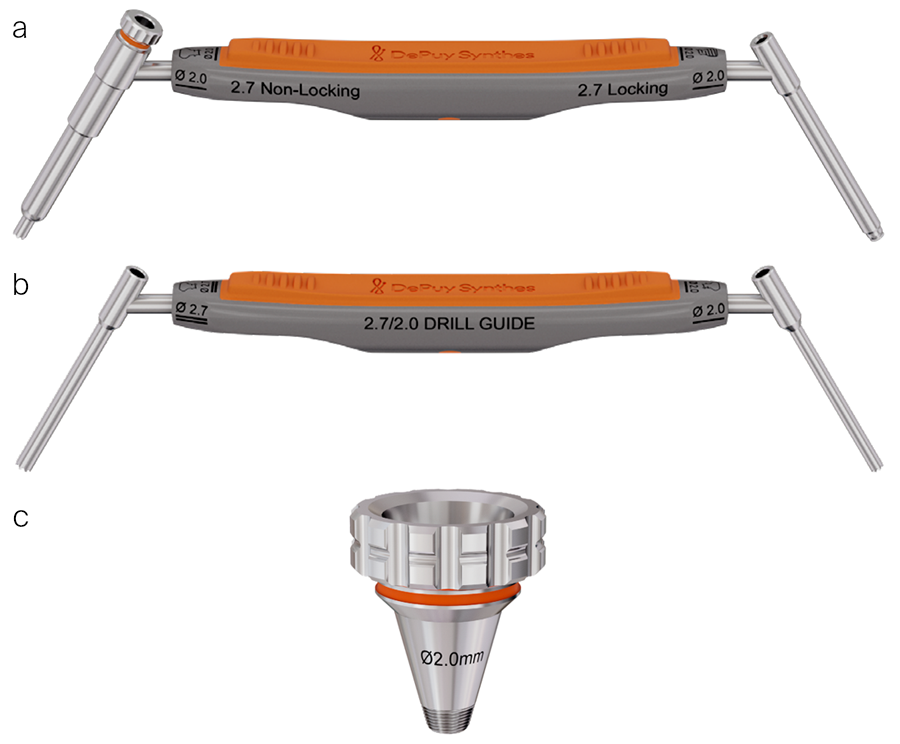
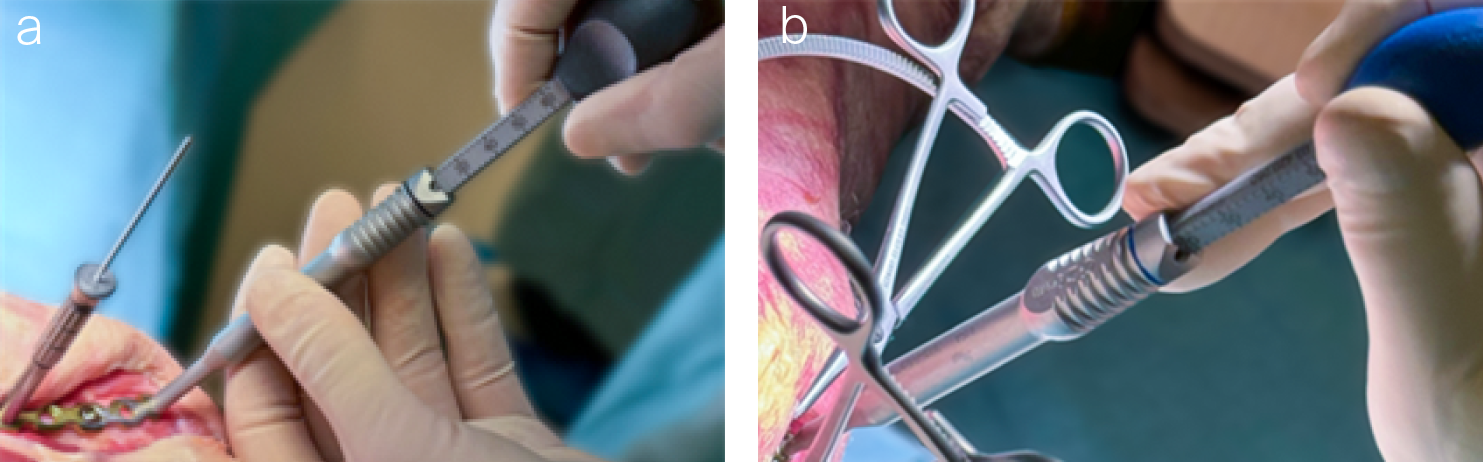
During the development of the threaded drill guides, special care was taken to allow for easy attachment to plate holes, even in plates bent within the bending guidelines. Handling of the threaded drill guide, including insertion and removal, can be supported with the screwdriver in the following sizes: 2.4 mm, 2.7 mm, and 3.5 mm (Fig 24).
Insertion and removal of the threaded cone drill guide is enhanced by a dedicated inserter (Fig 25).
Drill guides and their function
VOLT Cortex/Locking Double Drill Guide
• The locking end of the VOLT Cortex/Locking Double Drill Guide is used for free-hand variable angle drilling for locking screws.
• The non-locking end of the VOLT Cortex/Locking Double Drill Guide can be used for neutral and eccentric drilling in the DCU.
VOLT Double Drill Guide
• The VOLT Double Drill Guide is used for drilling for cortex screws, within a plate hole or independent of a plate, and can also be used for drilling the glide hole in a lag screw technique.
VOLT Threaded Cone Drill Guide
• The VOLT Threaded Cone Drill Guide can be used to limit drilling within the 30° allowed for locking screws.
Color coding
Color-coded universal and size-specific instrument and implant trays help the surgeon and the tech staff to select the right instruments for the selected plates (Annex Figs 28–32).
• Mini 2.0 mm — blue
• Mini 2.4 mm — purple
• Mini/Small 2.7 mm — orange
• Small 3.5 mm — black
Plate contouring (cutting and bending)
The different cutting and bending instruments can be used to contour and size the plate(s) to the fracture and patient anatomy. Prebending or contouring can be a useful technique to achieve adequate compression across the entire fracture surface.
The newly developed bending pins for the 2.0 mm and 2.4 mm plates can be used to bend the plates either prior to insertion or in-situ.
Postoperative treatment
Postoperative treatment with VOLT Mini and Small Fragment plates and screws does not differ from conventional internal fixation procedures.
General information
The VOLT system is not yet registered in all markets. It will be released progressively in different markets.
The VOLT Mini and Small Fragment systems are base platforms with a wide range of generic plates and applications. They will be progressively supplemented with anatomical preshaped plates that also utilize VOLT technology. Over time, it is envisioned that the VOLT Platform will gradually replace existing LCP and VA-LCP plating systems.
Annex
VOLT instruments overview
All instruments are color coded according to the size of the implants. Instruments which can be used for different sizes are grey.
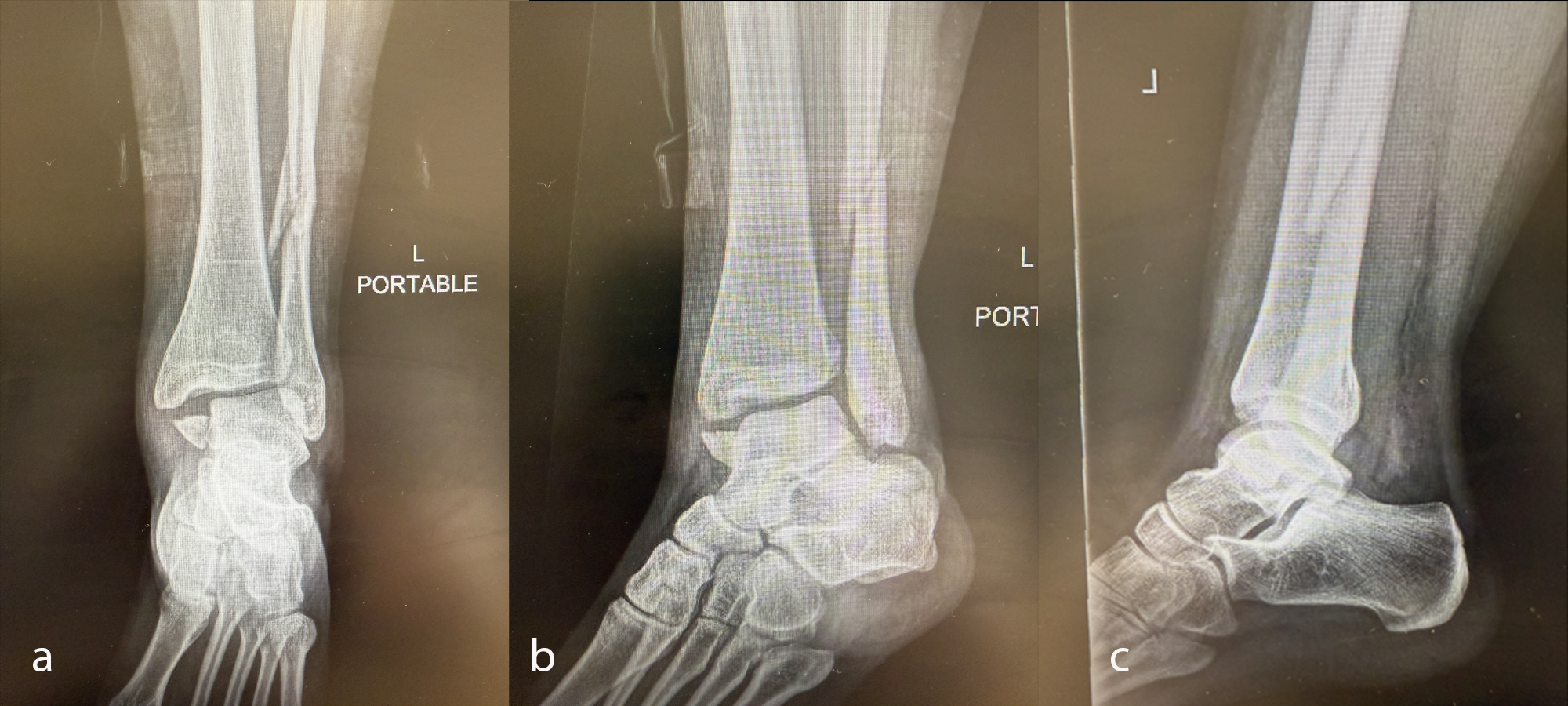
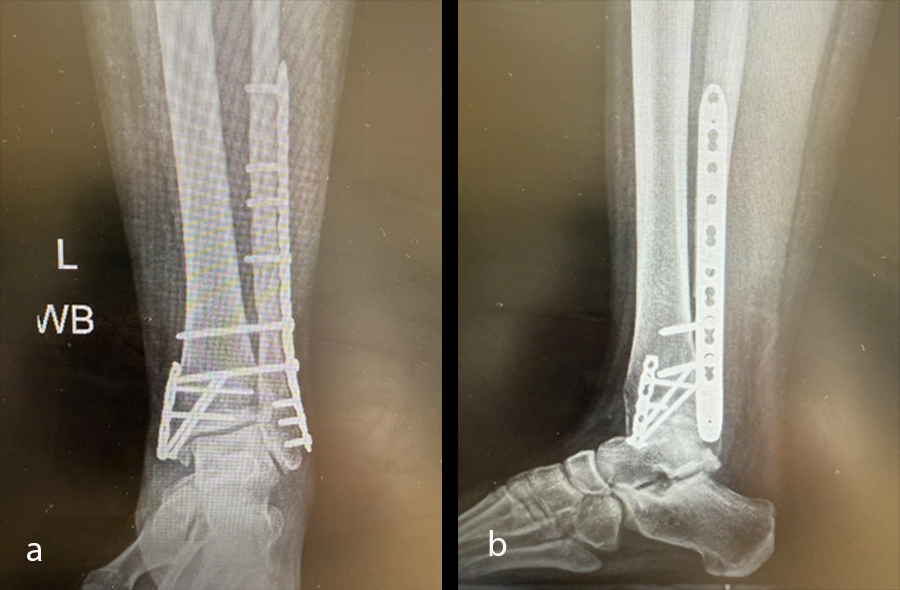
Case kindly provided by Andrew Sands, MD. New York Downtown Orthopaedic Associates, USA
A young adult had an accident, sustaining a trimalleolar ankle fracture with syndesmosis disruption (Fig 33).
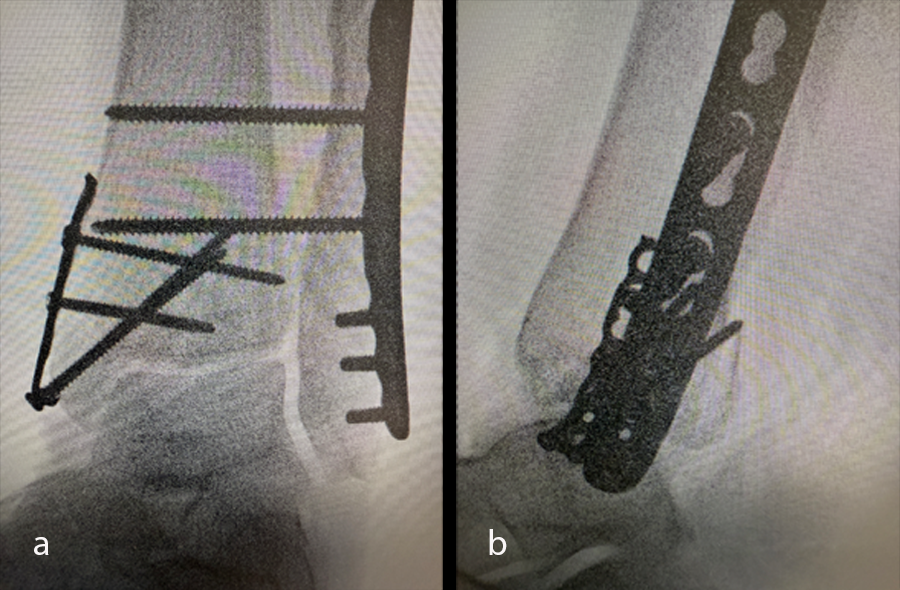
Once the soft-tissue swelling had reduced sufficiently, the patient underwent open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) surgery, with the VOLT™ Mini Fragment hook plate medially and the Small Fragment metaphyseal plate laterally. The syndesmosis was addressed with 4.0 mm screws (Fig 34). The surgery was uneventful and performed on an ambulatory basis.
At the 2-week postoperative follow-up, the splint was removed and the wounds assessed. The patient was then placed into a controlled ankle motion (CAM) boot and was advised to maintain nonweight bearing and start to gently increase range of motion in her ankle and hindfoot.
At the 6-week postoperative follow-up, the patient reported no pain and was advised to start progressive weight bearing with formal physiotherapy, and progressed from the CAM boot to a cushioned heel, rocker bottom shoe. X-rays taken at this time (Fig 35) showed good position of hardware and the fracture with signs of early healing.
At subsequent follow-up visits, the patient was doing well with full weight bearing and normal gait. The treatment plan is to remove the syndesmosis screws at 6 months postoperative or when convenient for the patient. As the screws are 4.0 mm, they are less likely to break. However, should screw breakage occur, the evidence [1] shows there is no disadvantage if they are removed from medial and lateral aspects of the ankle, or if the screw fragments are left in place.
References
- Schepers, T. To retain or remove the syndesmotic screw: a review of literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:879–883.
VOLT™ Mini Fragment and Small Fragment Plating Systems
This session may contain graphic medical procedures and imagery intended for educational purposes. Viewer discretion is advised. The content is designed for healthcare professionals and may include sensitive or disturbing material.
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.