Medial High Tibial Plate (TomoFix Anatomical)
Michael Blauth, Hiroaki Minchara, J Spence Reid, Steffen Schröter, Theodor F Slongo
The new generation of joint preserving technology TomoFix Anatomical
Joint-preserving therapies and specifically realignment osteotomy have been steadily gaining importance over the past decade. The combination of malalignment and unicompartmental osteoarthritis, most often encountered on the medial side, is a common problem which arises in all age groups. The high tibial osteotomy (HTO) is an established procedure for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis and can be performed through either an additive open wedge approach or a subtractive closed wedge procedure.
In 2001, the Knee Expert Group (KNEG) and AOTK in collaboration with Synthes, approved the world's first open wedge high tibia valgisation osteotomy system with plate fixator. It was named TomoFix and has remained a global market leader in the field of joint preservation and knee osteotomy for fourteen years.
Earlier this year, the AOTK approved a next generation of TomoFix in the form of a new Medial High Tibial Plate indicated for:
- Unicompartmental medial or lateral gonarthrosis with malalignment of the proximal tibia.
- Idiopathic or posttraumatic varus or valgus deformity of the proximal tibia.
The TomoFix knee osteotomy system is based on the trusted locking compression plate (LCP) technology, enabling angular stable connections between the screws and the plate. This angular stability allows the stable fixation of an osteotomy intended for early and safe mobilization in accordance with AO principles.
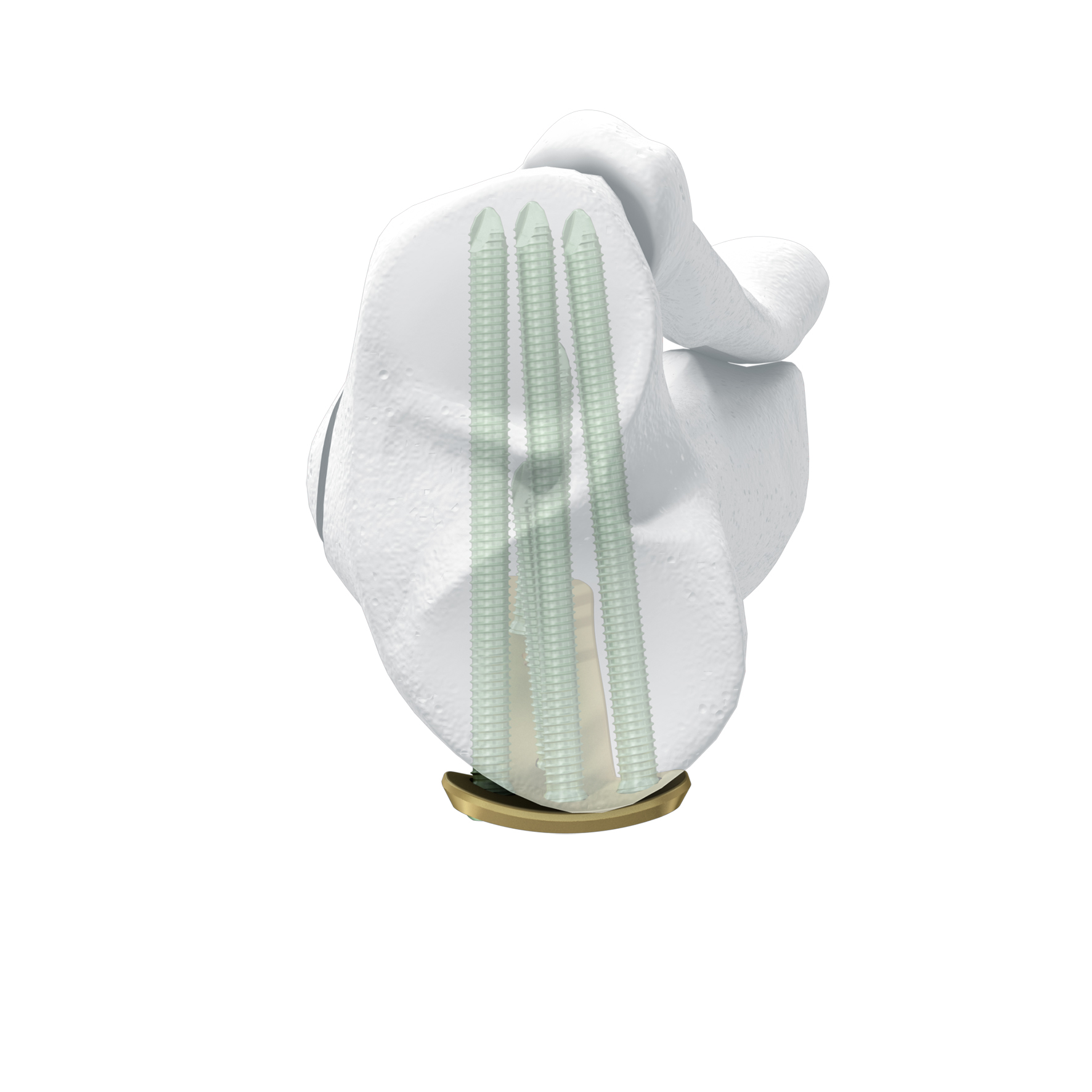
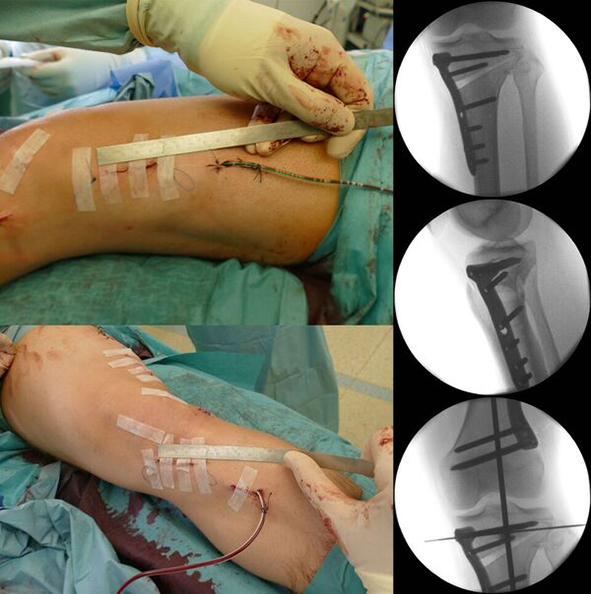
The TomoFix Anatomical Medial High Tibial Plate is contoured to provide an anatomical fit. When compared with the TomoFix Standard and small plates, the new design is intended to reduce both implant prominence
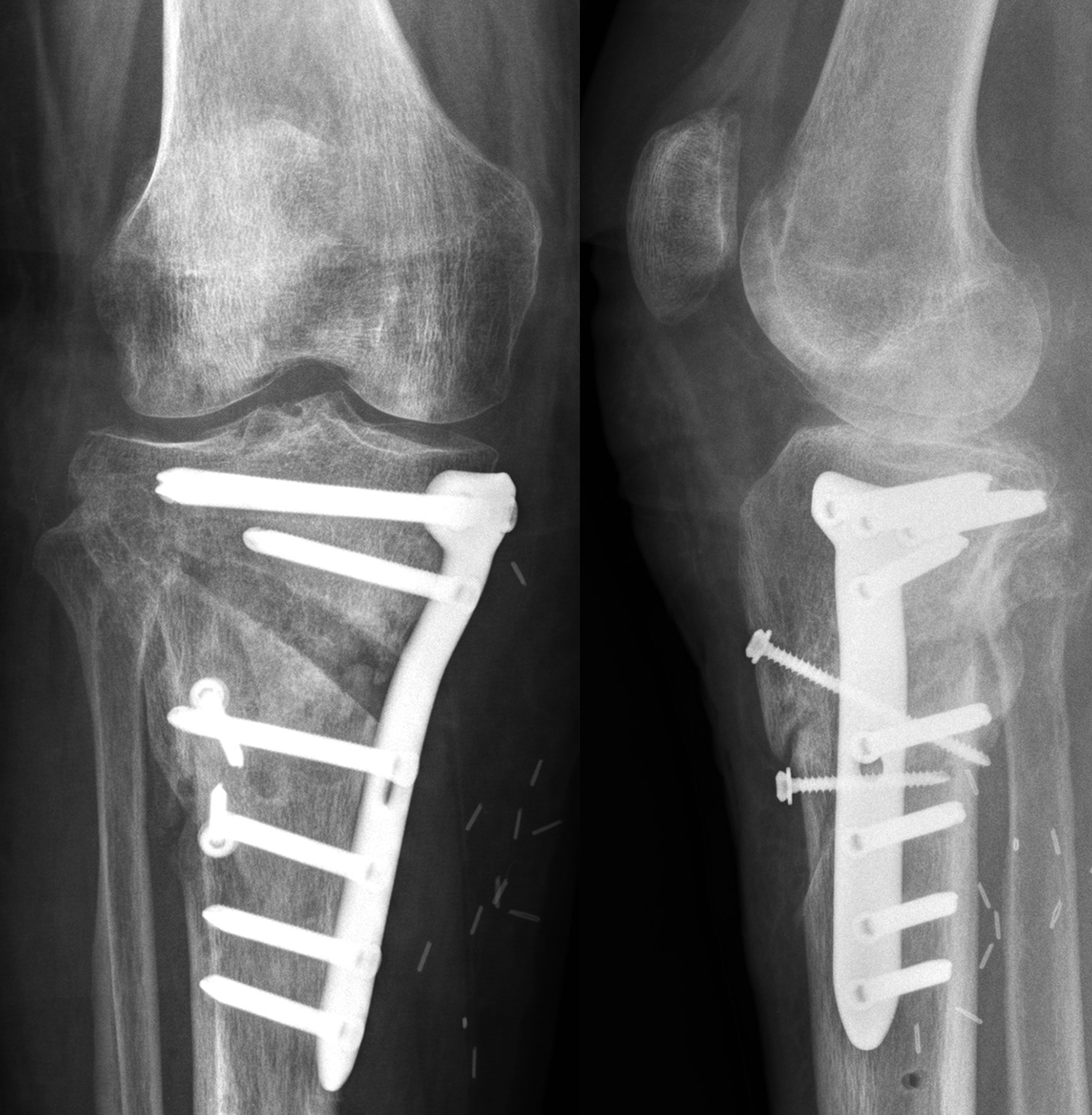
and postoperative implant irritation. Fig 1 shows x-rays from one patient.
Features
Features include:
- The 5° slant of the plate helps achieve parallel fixation of the proximal plate to the plateau slope of smaller statured tibia (Fig 2)
- The new plate shape facilitates plate placement towards the medial side, providing support on the medialposterior edge of the tibial plateau. This also functions to help prevent neurovascular damage
caused by possible screw protrusion (Fig 3) - The TomoFix MHT plate is designed to accommodate both small and large oblique osteotomies
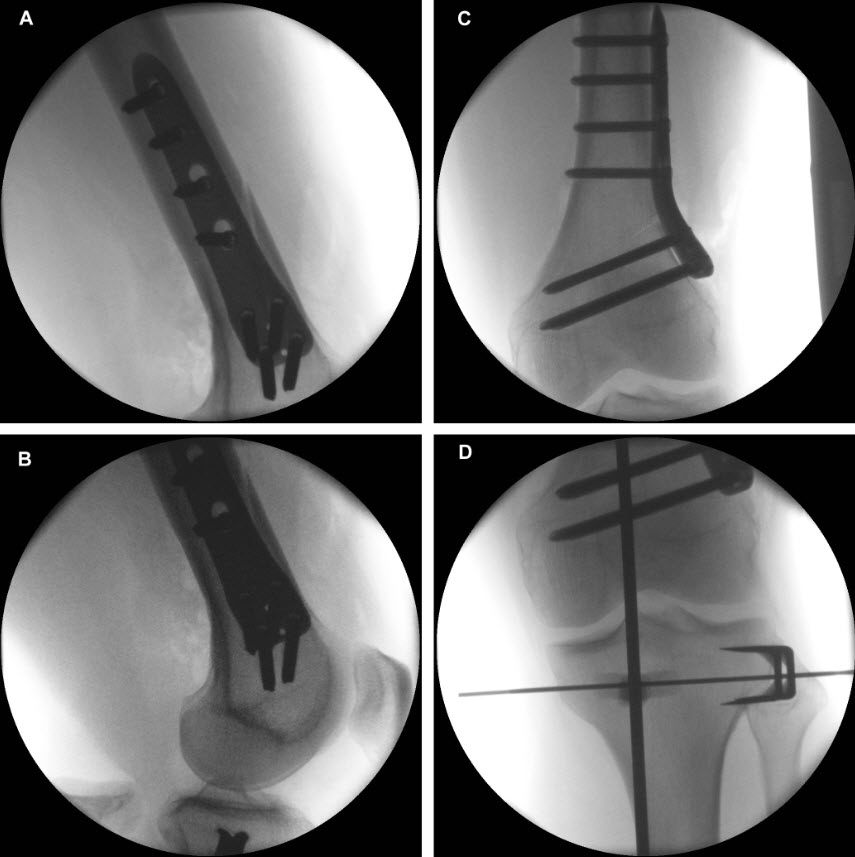
Not only does the new TomoFix Knee Osteotomy System contain a new MHT plate with more anatomical features, it also includes new osteotomy instrumentation intended to improve both surgical accuracy and procedural efficiency. The new instrumentation is compatible with the existing Standard and small TomoFix Medial High Tibia plates. Fig 4 shows a patient with post-traumatic deformity after a proximal tibial fracture (at the 6-week follow-up after open wedge HTO in descending technique and fixation with the TomoFix MHT anatomical plate).
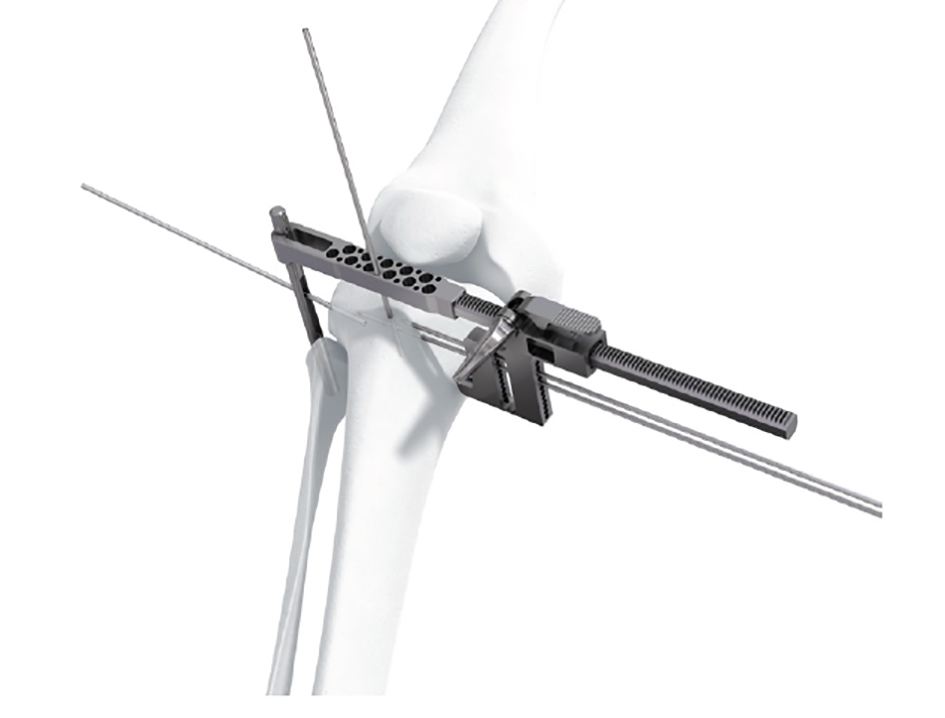
High tibial osteotomy is a technically demanding procedure. Complications commonly include postoperative malalignment, imprecise correction, and damage to the tibial dorsal neurovascular structures. Correcting malalignment to the desired angle with precision is a key element of the surgery. The new TomoFix Osteotomy Instrumentation is intended to assist surgeons to define the osteotomy line and maintain steady sawing during the osteotomy cut. Additionally:
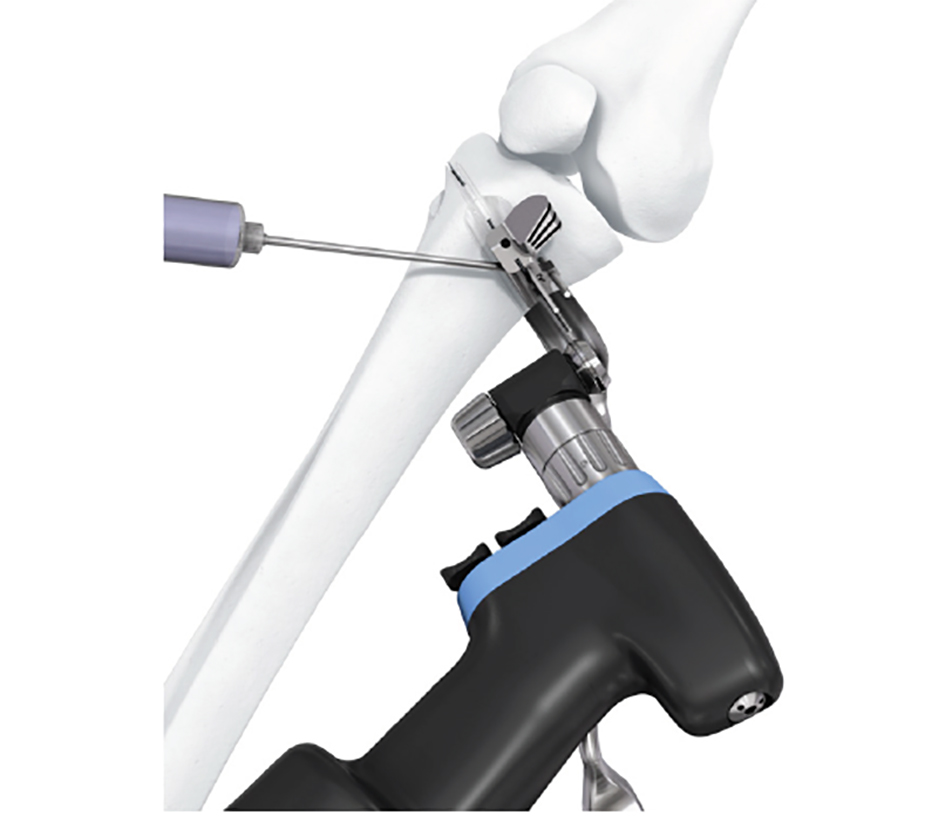
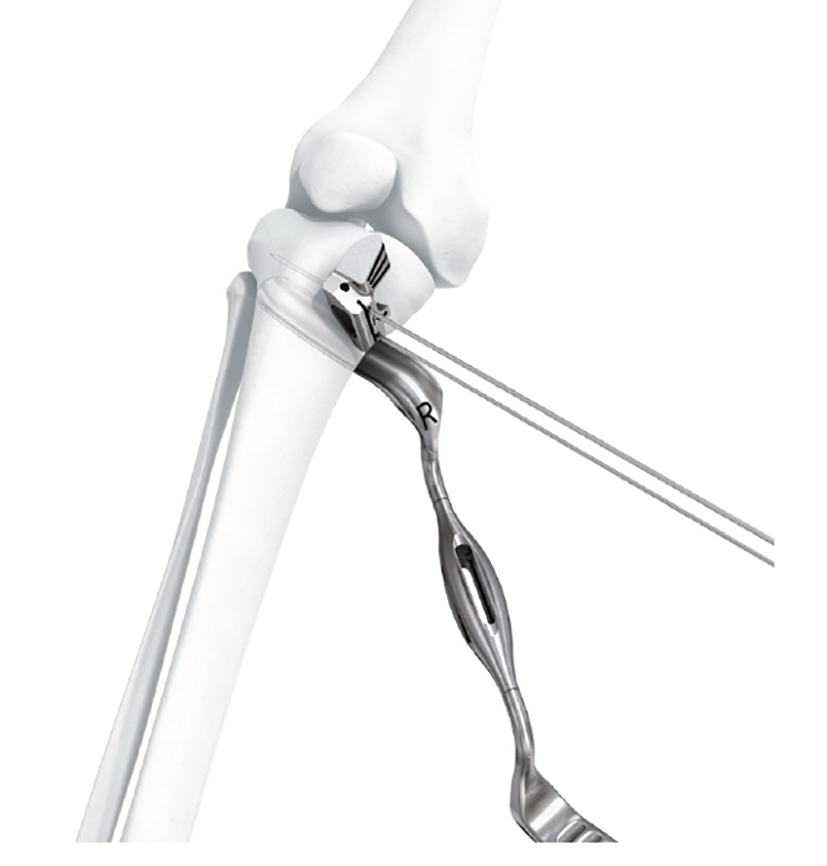
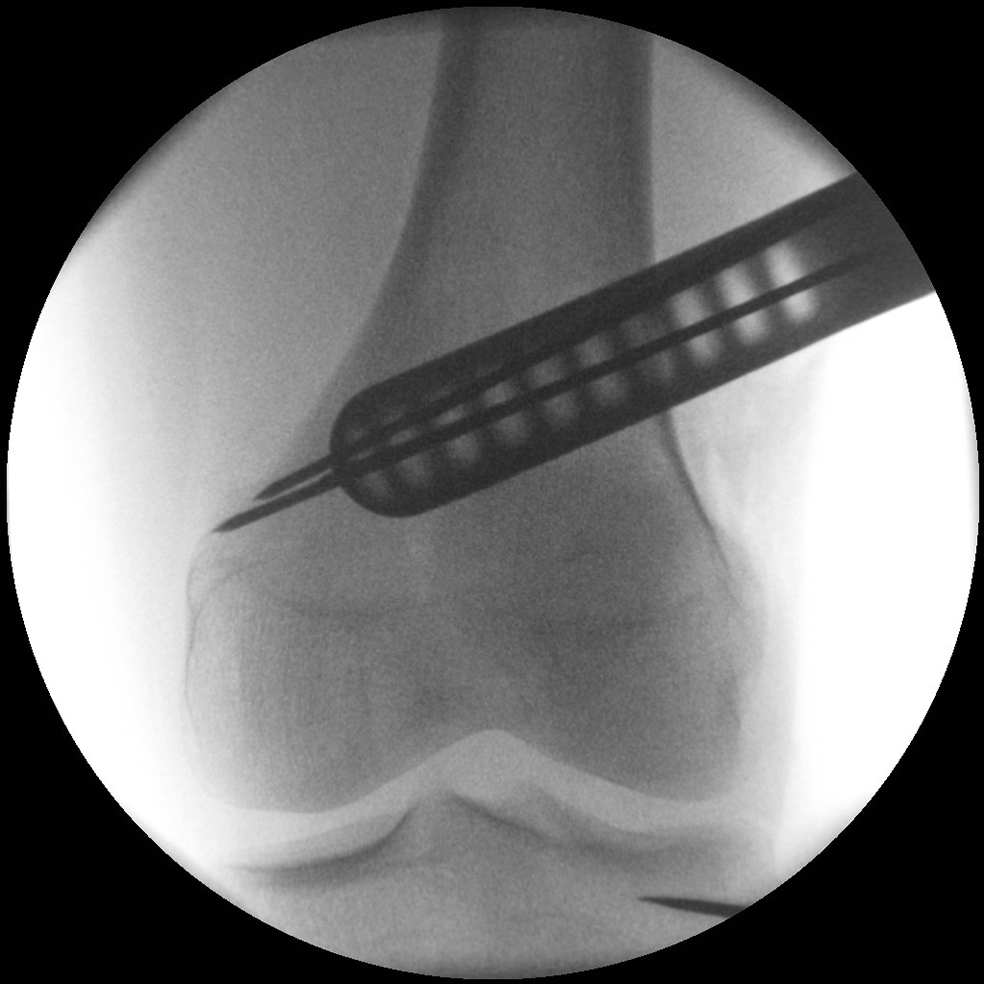
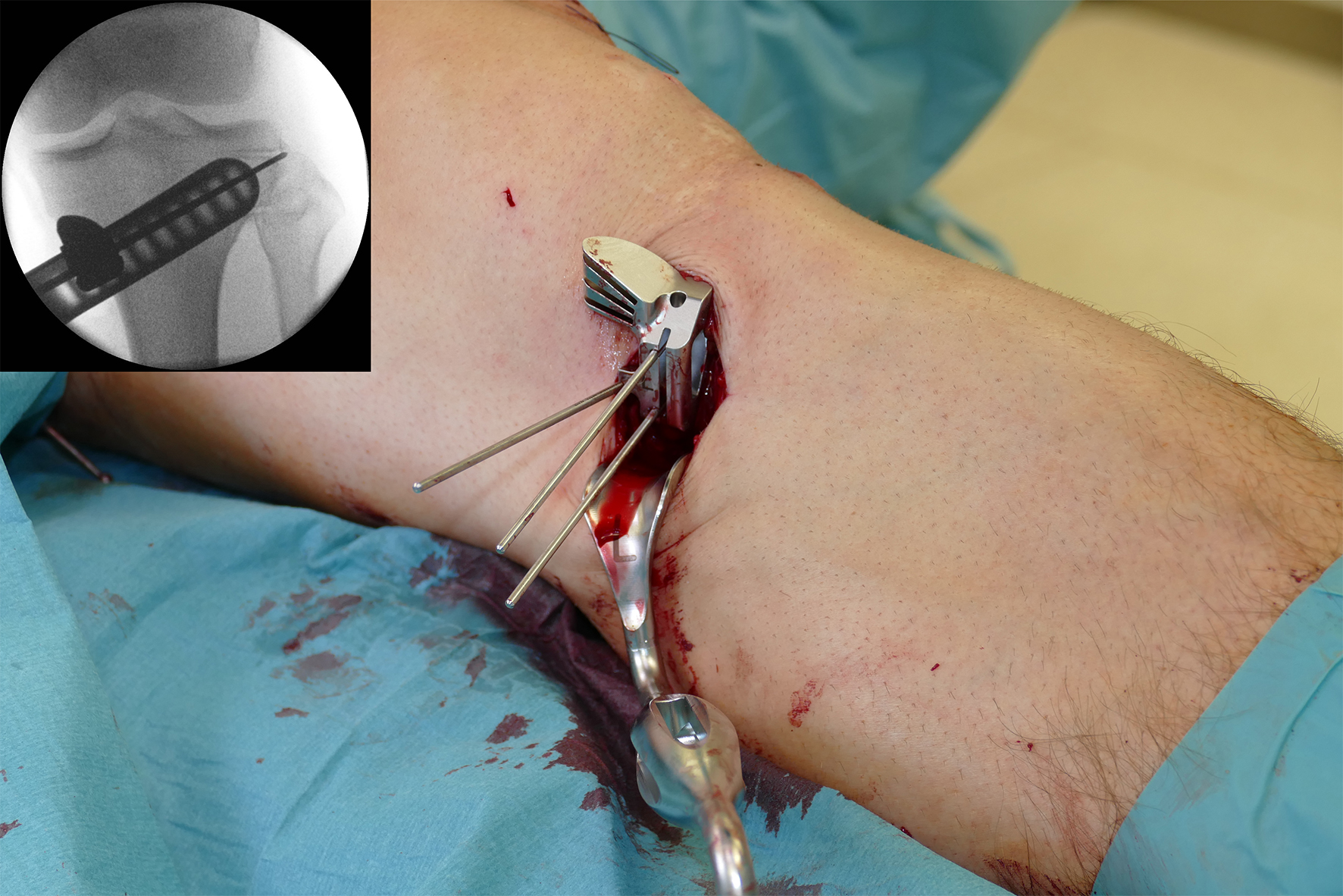
- The aiming arm and K-wire guide support the insertion of K-wires to help maintain tibial slope and aim at the hinge points (Fig 5)
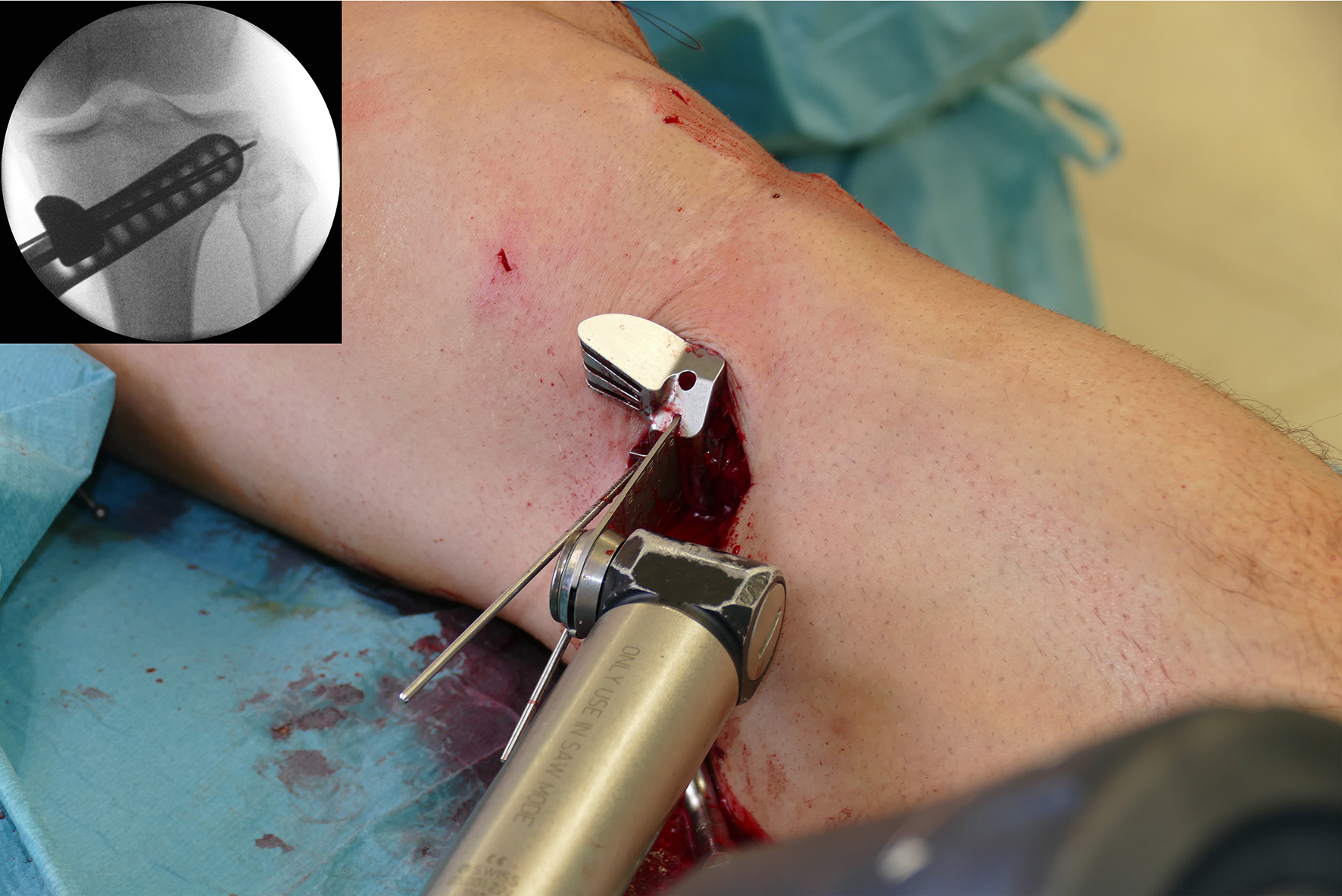
- The saw guide allows surgeons to perform biplanar osteotomy under x-ray guidance (Fig 6)
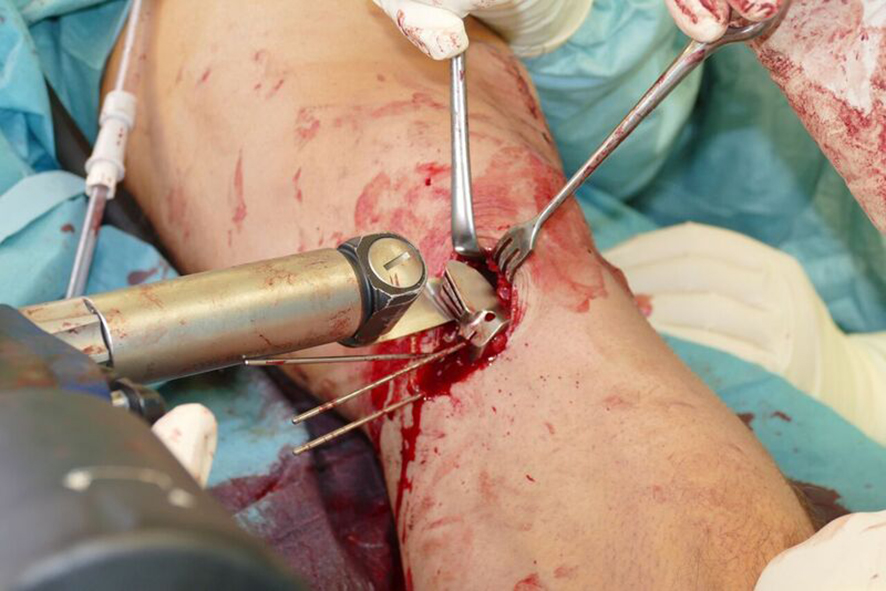
- The radiolucent retractor is intended to protect the posterior neurovascular structures while sawing (Fig 7)
Case: Knee pain following epiphysiodesis
Case provided by Steffen Schrter, Tbingen, Germany
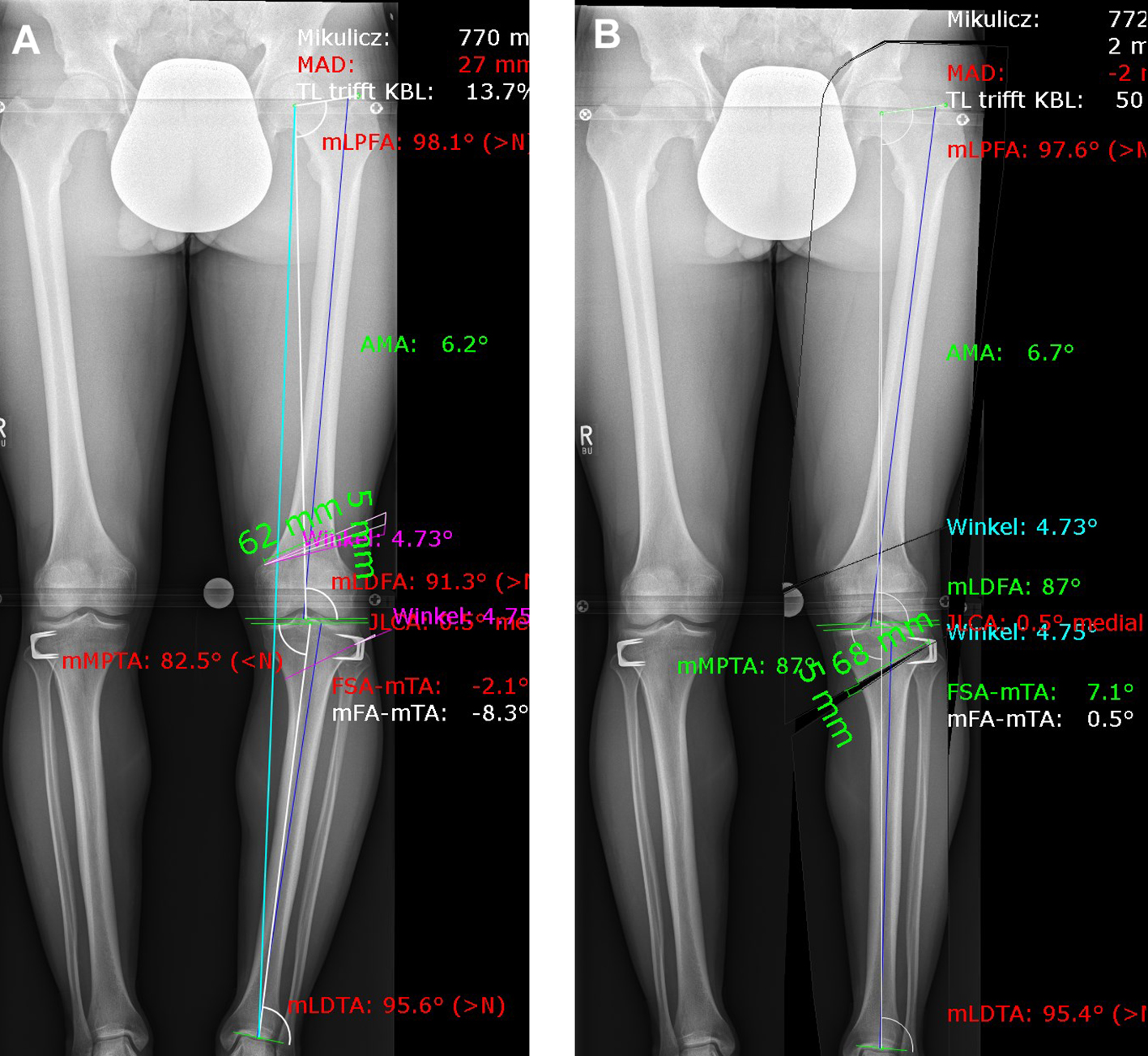
A patient presented with a congenital varus malalignment and complained of medial knee pain following epiphysiodesis at the proximal tibia. The MRI showed no cartilage lesion. A varus deformity of -8 in conjunction with medial knee pain was the indication for surgery. Fig 8 presents the deformity analysis of the left knee. Because of the deformity in the distal femur and proximal tibia, a double level osteotomy was planned and digitally simulated. The image on the left shows a combined deformity comprising a mechanical tibiofemoral angle (mTFA) of -8, a mechanical lateral distal femur angle (mLDFA) of 91, and a mechanical medial tibia angle (MPTA) of 83 (A). The image on the right shows the simulation of a double level osteotomy (B). Aim was a mTFA of 1 (valgus), a mLDFA of 87, and a MPTA of 87. The distal femur osteotomy was planned as a closed wedge distal femoral osteotomy (DFO) and the tibia osteotomy was planned as an open wedge HTO.
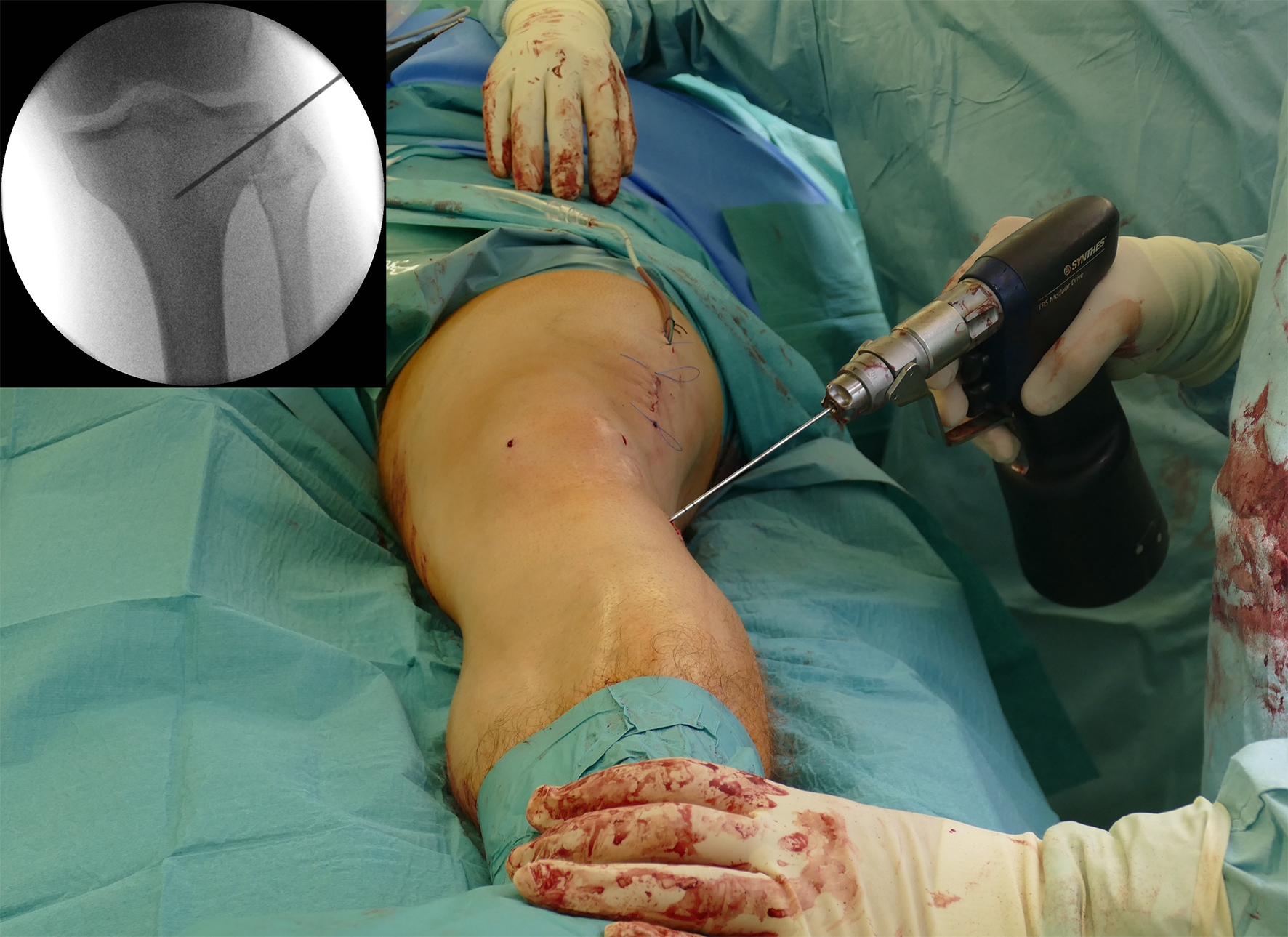
Surgery was initiated with an arthroscopy. No cartilage lesion was observed and removal of the lateral staples followed. The osteotomy started at the femur as a lateral closed wedge biplanar DFO. The new radiolucent hook from the TomoFix Anatomical system was tested during this aspect of the procedure. The hook is ideal in the adoption of a minimally invasive approach for use in patients with normal soft tissue (Fig 9).
Following completion of the DFO and fixation with the TomoFix MDF Anatomical (Fig 10) the new aiming arm and K-wire guide system was used for the open wedge HTO.
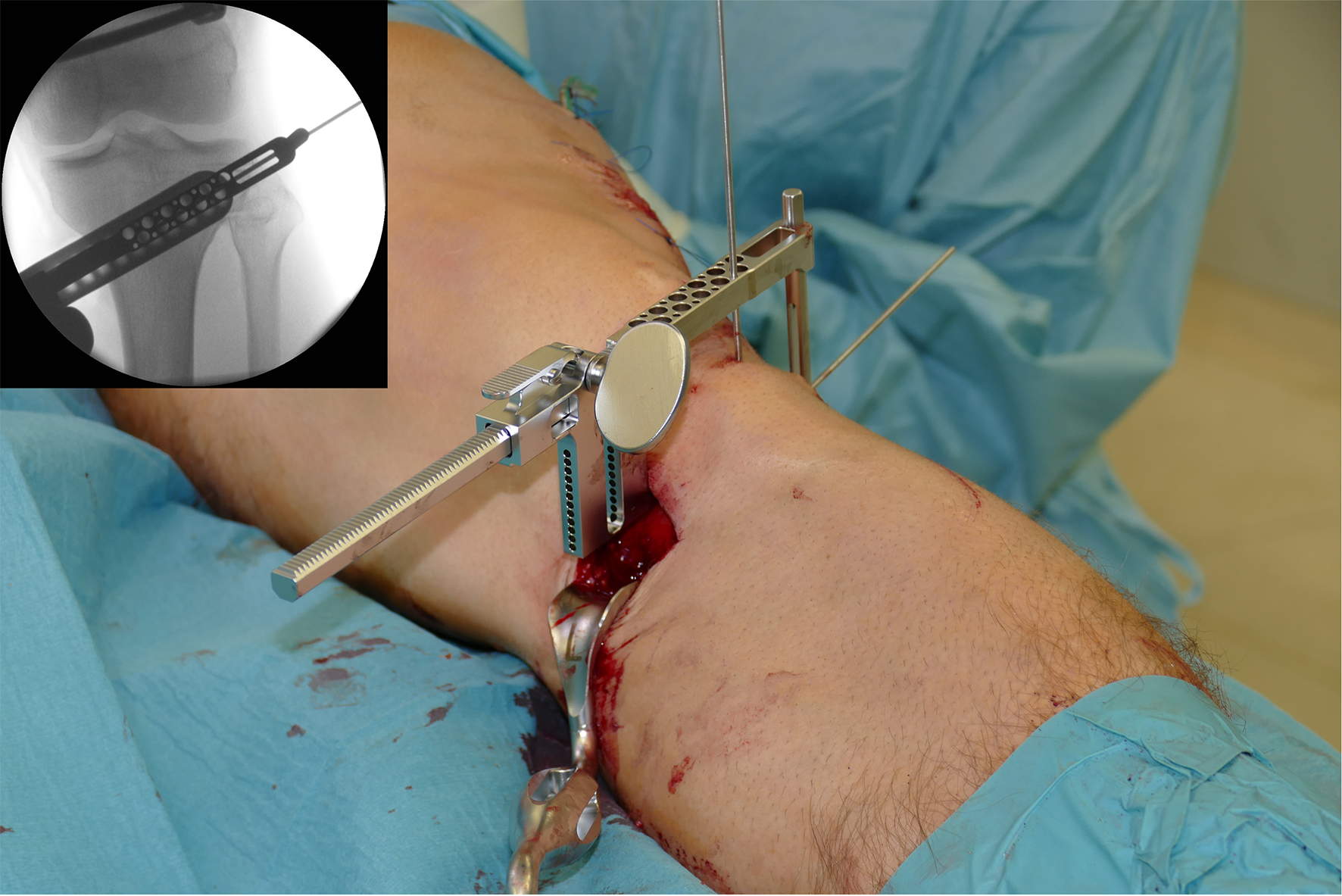
After performing a minimally invasive approach at the medial proximal tibia, the first step of the new K-wire guiding system is definition of the hinge point with a K-wire from the lateral aspect (Fig 11). The guiding arm for the osteotomy was then inserted with the radiolucent hook in situ (Fig 12). The guiding arm should be adjusted under intensifier control and finally fixed with a K-wire. At this stage two K-wires for the osteotomy can be inserted and the guiding arm can be removed. The saw guide is then mounted and guides the sawblade safely (Fig 13 and 14).
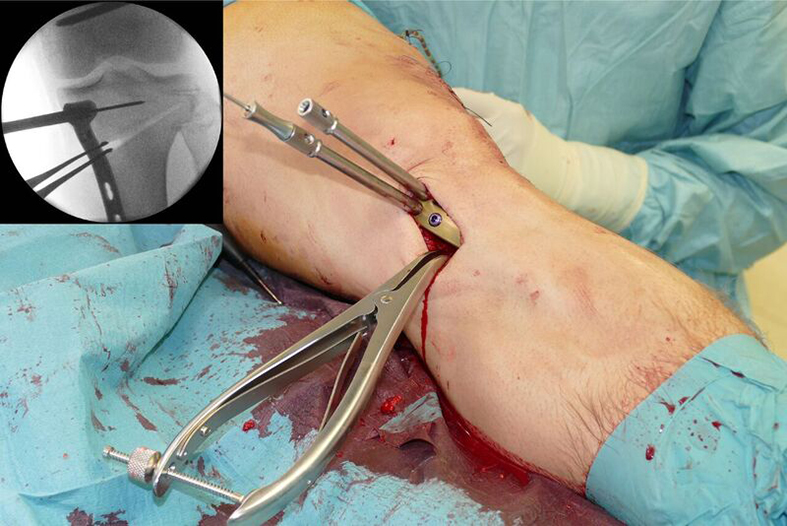
The saw guide enables three different angulation options for the ascending cut (Fig 15). Following completion of the osteotomy, the opening is performed in the traditional way using chisel and spreader. Fixation is performed with the new TomoFix MHT Anatomical plate (Fig 16 and 17).
Innovations in osteotomies around the knee
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.