MatrixWAVE MMF
Carl-Peter Cornelius, John Hardeman
Maxillomandibular fixation (MMF) is a vital step in the management of maxillofacial trauma. In order to fixate fractures correctly and achieve adequate fracture reduction, the maxillary and mandibular dentition must be aligned in occlusion. Various methods can be used to achieve MMF including Arch Bars secured with interdental wires and IMF screws, but these methods have several disadvantages (listed in "Details", below).
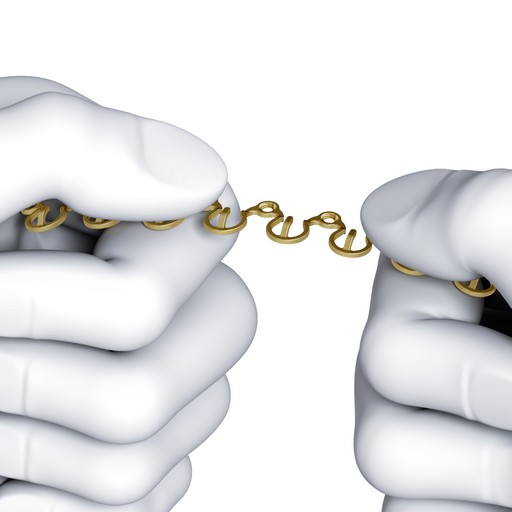
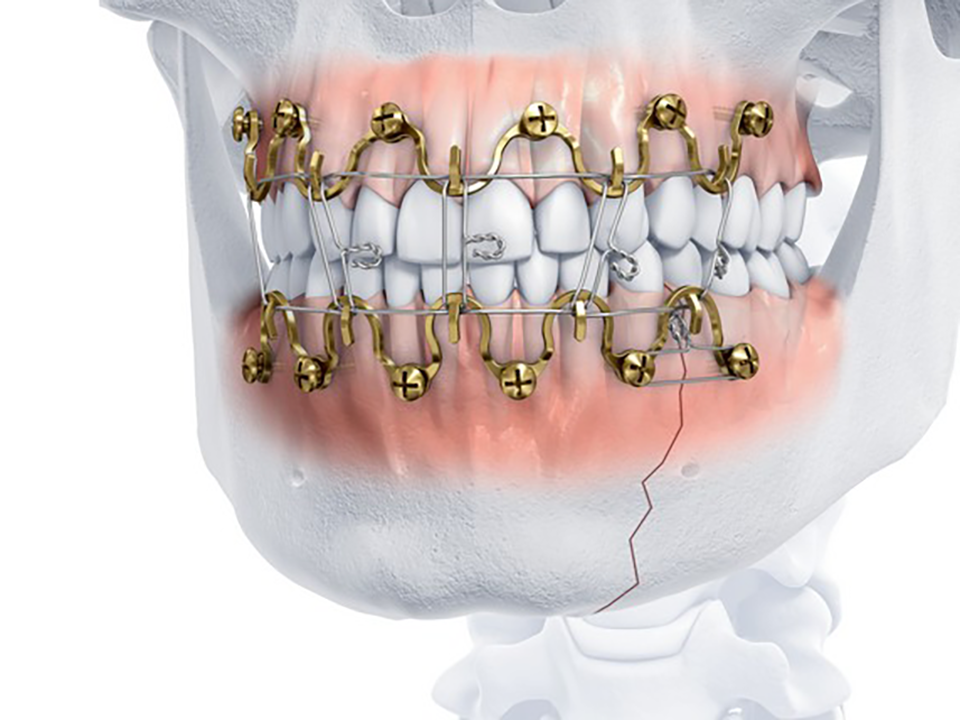
MatrixWAVE MMF (Figs 1-8) is a novel bone-borne MMF system that combines the strength and rigidity of arch bars with the speed and simplicity of IMF screws. It consists of a wave shaped plate that is attached to the mandible and maxilla with self-drilling locking screws (Fig 3). The plate is adaptable and can be extended horizontally (Fig 4) to allow screw hole placement in the optimal location to avoid tooth roots and nerves. The locking mechanism avoids compression and ischemia by keeping the plate away from the mucosal tissues.
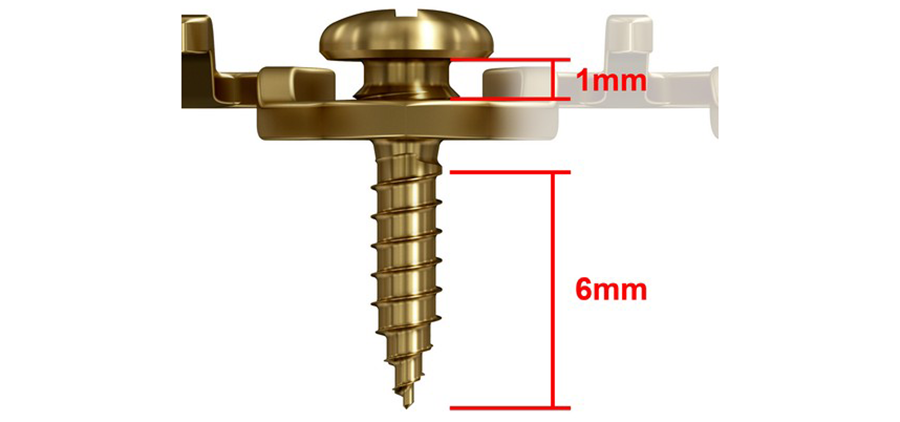
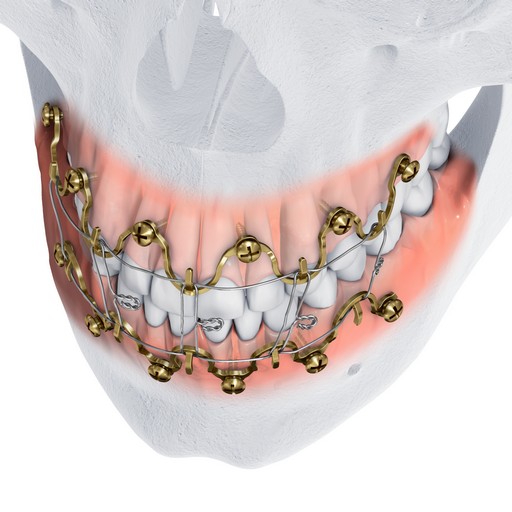
The dental arches are brought into occlusion by wiring around the plate hooks and/or accessible screw heads. The self-drilling locking screws sit proud to the plate. This minimizes soft tissue growth over the screw, and provides additional anchor points for optional bridle wires. Upon insertion, screws can be angled at up to 15 to aid in posterior fixation and to optimize dental occlusion.
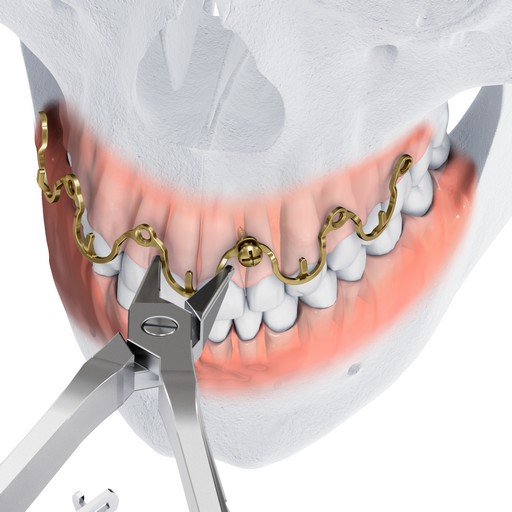
Following application and wiring, the wave plate pattern allows the alignment of bone segments to be adjusted by crimping without repositioning the screws. The plate is available in two heights to allow the positioning of the hooks at the level of the tooth equators according to individual patient anatomy, and to accommodate the use of rigid internal fixation (Fig 2).
Limitations of arch bars
Limitations of arch bars include prolonged operating room time and expense to apply and remove the device; difficulty in fragment alignment once the arch bar has been put in place; high incidence of needle stick type injuries; difficulty in maintaining oral and gingival hygiene; and the risk that tightened wires may cause ischaemic necrosis of the mucosa and periodontal membrane, causing tooth loss.
Limitations of IMF screws
Limitations of IMF screws include posterior mandible fractures being more prone to poor reduction and subsequent malocclusion; and the risk of unnoticed lingual tilting of fragments due to the distance between anchoring points.
Design features and benefits
Maxillomandibular fixation can be achieved more quickly using the Matrix WAVE plate than by using arch bars. Removal is simple, and can be done in a non-OR setting. The MatrixWAVE plate design eliminates the need for circumdental wiring. This has several advantages, including reduced risk of needle stick-like injuries and reduced risk of tooth loosening. Additionally, the MatrixWAVE MMF system covers less tooth surface, allowing more access to the teeth for cleaning. The design of the plate maximizes patient comfort, as it has rounded, smooth edges. The screw heads are also rounded, and the plate hooks can be bent towards the gingiva after wiring.
Indications
The MatrixWAVE MMF System is indicated for the temporary stabilization of mandibular and maxillary fractures and osteotomies in adults and adolescents (age 12 years and higher) with full permanent dentition. The system is intended to maintain proper occlusion during intraoperative bone fixation and postoperative bone healing (approximately 6-8 weeks). The system affords the ability to align bone fragments. However, MatrixWAVE MMF plates do not have a tension band function, unless additional bridle wire loops are used on the screw heads across the fracture line.
Clinical Case
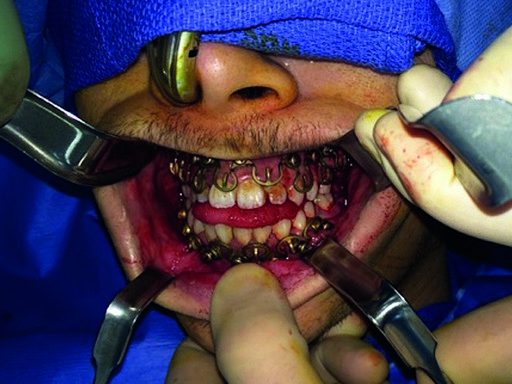
A 28 year old white male was subject to personal assault, and sustained a left mandibular angle fracture (Fig 1). The fracture was prestabilized with the Matrix Wave system and then fixated with a 4-hole miniplate 2.0 on the superior border and a 4-hole angulated universal fracture plate 2.4 along the inferior border. A pre-existing anterior open bite was noted and confirmed with the patient prior to presentation to the operating arena.
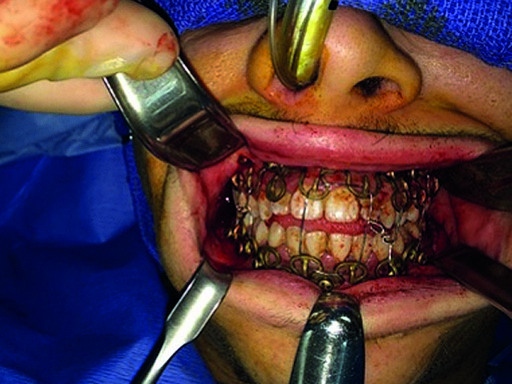
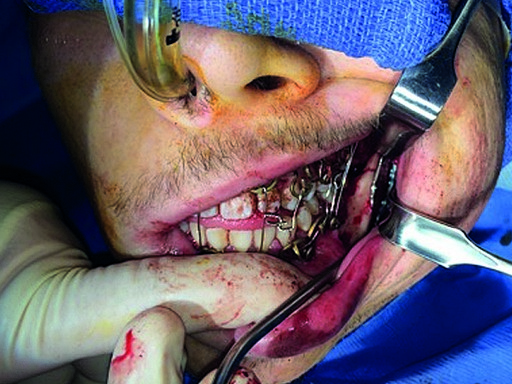
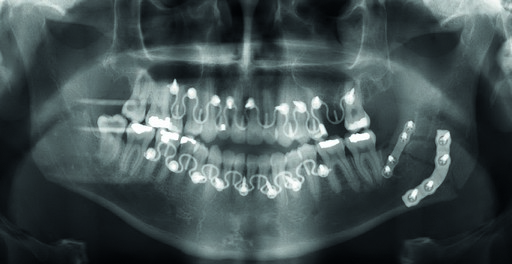
The MatrixWAVE plate was attached to the maxilla with screw placement in the inter-root spaces (Fig 2). A second MatrixWAVE plate was attached in corresponding position to the mandible, with screw placement in the inter-root spaces (Fig 3). Wires were placed around the plate hooks to bring the dental arches into occlusion. Note the preexisting anterior open bite (Fig 4). Careful adjustment of the MatrixWAVE plate and wiring in the region of the mandibular fracture allowed the bone fragments to be precisely aligned without the requirement for screw repositioning (Fig 5). The postoperative panoramic x-ray (Fig 6) shows the two MatrixWAVE plates in situ, with other plates used to fixate the left mandibular angle fracture. Note that a portion of the Matrix- WAVE plate was removed from the left molar region in the mandible (Fig 6).
Innovations in Maxillomandibular Fixation
MatrixWAVE Value Analysis Brief
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.