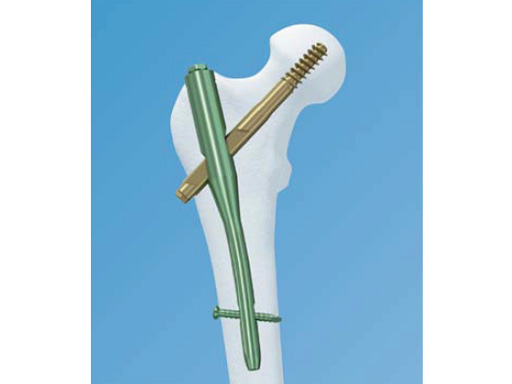
Trochanteric Fixation Nail (TFN)
The TFN is a new cannulated, intramedullary nail system. It is indicated in stable and unstable fractures of the proximal femur including pertrochanteric, intertrochanteric, basal neck fractures, as well as a combination thereof. Additionally, the long TFN is indicated in high and long subtrochanteric fractures, pertrochanteric fractures associated with an injured shaft, pathological fractures (of osteoporotic bone) in both trochanteric and diaphyseal areas, proximal or distal nonunions, malunions, and revisions.
The helical blade provides improved resistance to varus collapse and rotational control of the head-neck fracture segment. The result is superior life to cut-out versus single screw fixation and reduced bone removal versus a traditional hip screw.
The TFN is made of titanium alloy (Ti-6AI-7Nb). The TFN is available in two sizes, short in lengths of 170 mm and 235 mm, and long in lengths of 300460 mm. Additional to the existing diameters of 10 mm, 11 mm and 12 mm, the TFN is now also available in 14 mm diameter.
The 11.0 mm Titanium helical blade provides improved resistance to varus collapse and rotational control of the head-neck fracture segment. The result is superior life to cut-out versus single screw fixation and reduced bone removal versus a traditional hip screw. The helical blade is now available in additional lengths of 75 mm, 125 mm and 130 mm. A choice from 75130 mm in 5 mm increments en-ables selection of the appropriate blade according to the patients anatomy.
TFN with Screw
The TFN has been available with a spiral blade only, but will be offered with a screw as an optional femoral head element for those surgeons who are concerned about distraction of the fracture while impacting the TFN blade. This occurs very rarely in patients with dense, healthy bones.
AO has favored in the past, and will continue to favor, the spiral blade, since biomechanical research has demonstrated the advantages of the spiral blade compared to a screw, which includes preventing cutout and providing rotational stability.
The screw is self-tapping and will be available in a diameter of 11.0 mm in lengths of 70130 mm. Two flats allow an adjustability of 180. A slot aids control of rotation and the amount of screw travel.
Using the TFN with a screw instead of a blade requires these additional instruments: inserter/extractor, compression nut, and tap/reamer.
TFN Set Screw
Some surgeons like the option of preventing sliding of the TFN helical blade or screw in certain situations, such as, reconstructive procedures, gun shot injuries, reverse obliquity fractures, and tumors. In order to prevent collapse of the head element, the TFN Set Screw (Fig a) was developed. Once the set screw is tightened with a torque limiting handle, the grooves on the underside of the TFN Set Screw engage with the helical blade or screw to prevent sliding. It is available in 3 angles (125, 130 and 135) in order to match the CCD angle of the nails, and is made of TAN (alloy).
If a surgeon wants to prevent sliding, the scrub technician has to remove the TFN locking mechanism from inside the nail, on the back table, and replace it with the pre-assembled TFN Set Screw. The surgeon must make a conscious decision to replace the locking mechanism with the TFN Set Screw, which helps ensure the surgeon does not unintentionally prevent sliding.
Self-retention between subcomponents of the TFN Set Screw allows for ease of insertion. After the head element is inserted, the surgeon will use a torque limiting handle to tighten the set screw and prevent collapse. If the surgeon changes his or her mind and wants to allow sliding, the tang is long enough that the set screw can be backed off to allow sliding, while still preventing rotation. If sliding is permitted, however, an end cap must be used in conjunction with the set screw.
It is important to note that the TFN Set Screw should only be used for fixation in fractures where sliding of the head element is not desired. The addition of the locking feature expands the utility of the TFN system. While it should only be used in select cases, the new locking feature offers an alternative fixation option for certain difficult and complex fractures.
Instruments for Over-Insertion of the Helical Blade for Trochanteric Fixation Nail (TFN)
In certain clinical situations, the Helical Blade may be inserted beyond the lateral cortex of the femur. The Over-Insertion Instruments should only be used when more than five millimetres of interfragmentary compression is necessary. The lateral aspect of the Helical Blade will be flush with the lateral cortex. Indications are 31-A1 and 31-A2 fractures - excluding 31-A3 (reverse obliquity fracture) - done in all appropriate fracture patterns to achieve maximum compression at the time of surgery, minimizing the subsequent dynamization by the Blade with postoperative weight bearing , thereby creating a more stable fracture-implant construct at the time of surgery.
Note: Clinically and in osteoporotic cadavers in the lab, pull-out of the blade from the head via axial compression using the compression nut has not occurred.
A Counterbore was added to the central hole of the Buttress/Compression Nut to allow the Blade Guide Sleeve to be fully inserted to the level of the lateral cortex.
TFN Percutaneous Insertion Handle for Obese Patients
For soft-tissue clearance in very obese patients, the standard trochanteric fixation nail (TFN) insertion instruments may be too short, as the barrel of the standard insertion handle only measures 44 mm in length. Therefore, a longer barrel for the percutaneous insertion handle was designed with an increased length of 144 mm. The added length necessitates a longer mating connecting screw and a longer 5.0 mm hexagonal screwdriver to engage the TFN locking mechanism.
Because of its length a more proximal skin incision than typical is needed. By concentrating on a more proximal skin incision in the obese patient one might avoid the necessity to lengthen the skin incision and deep soft-tissue dissection with the existing jig.
This additional handle should not be used on a nonobese patient as the added length of the arm may impinge on the soft tissues making the insertion more difficult.
5.0 mm Flexible Hexagonal Screwdriver, Coated
The 5.0 mm flexible hexagonal screwdriver has a silicon-coated flexible screwdriver shaft which was designed specifically to improve cleaning. By impregnating the coils of the flexible shaft with silicon it creates a barrier to blood and debris. The coating increased the overall diameter of the screw driver shaft and also decreased its perceived flexibility.
Furthermore, the hexagonal design has been modified to allow the driver to find its way into the recess easily. The changed screwdriver tip has significantly improved the ease of engaging the TFN blade antirotation device for its ultimate delivery to engage the blade.
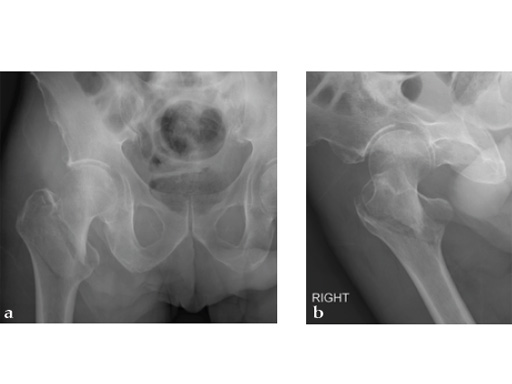
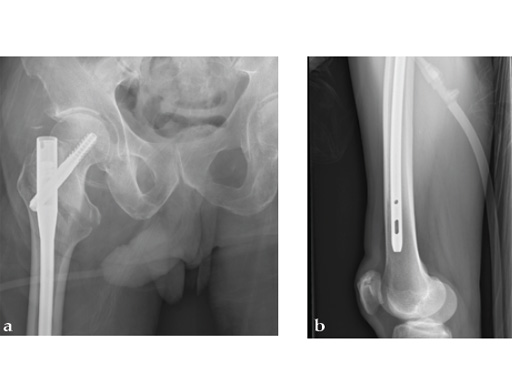
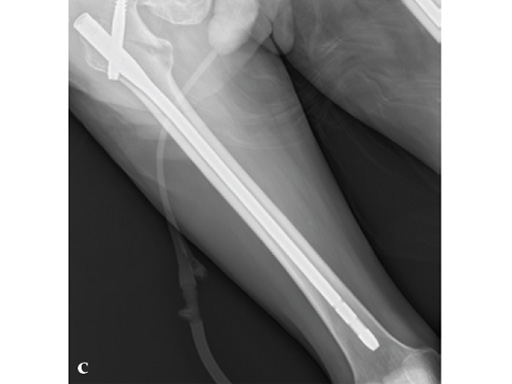
72-year-old female who sustained a closed intertrochanteric fracture in a car accident. The fracture was classified as an 31-A3-1. There were no other injuries reported.
Case provided by Cliff Turen, Macon, USA
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.